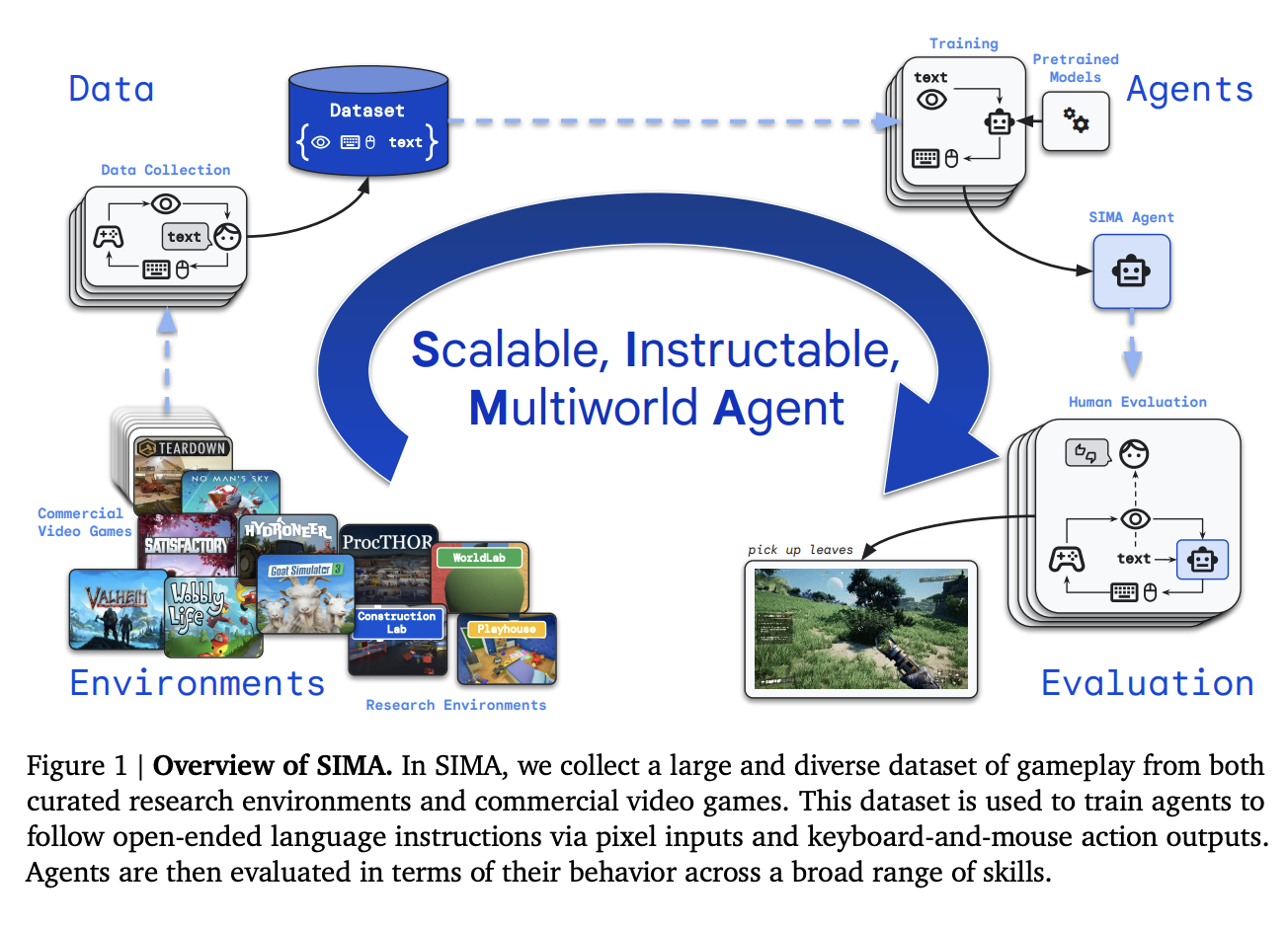
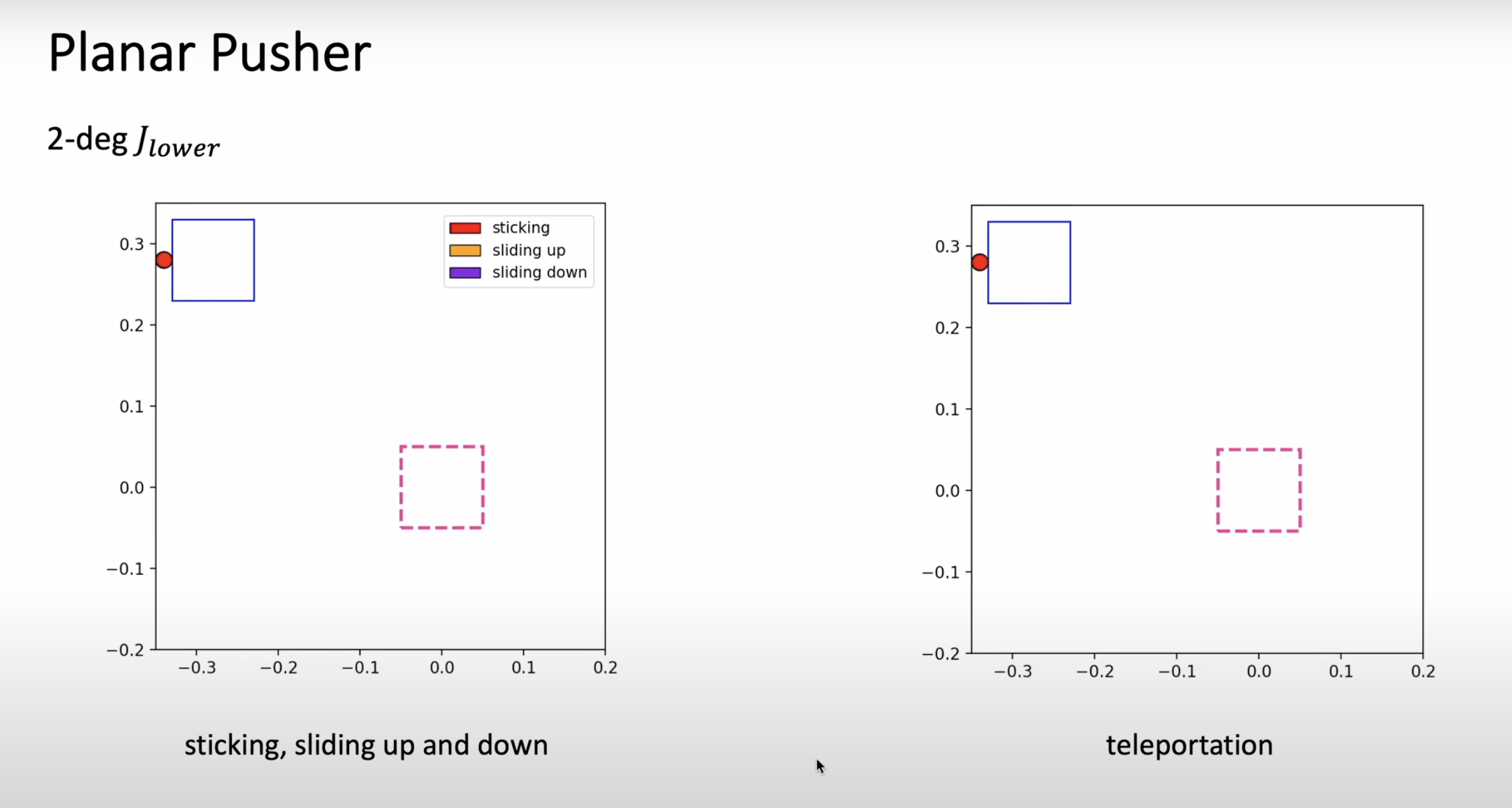
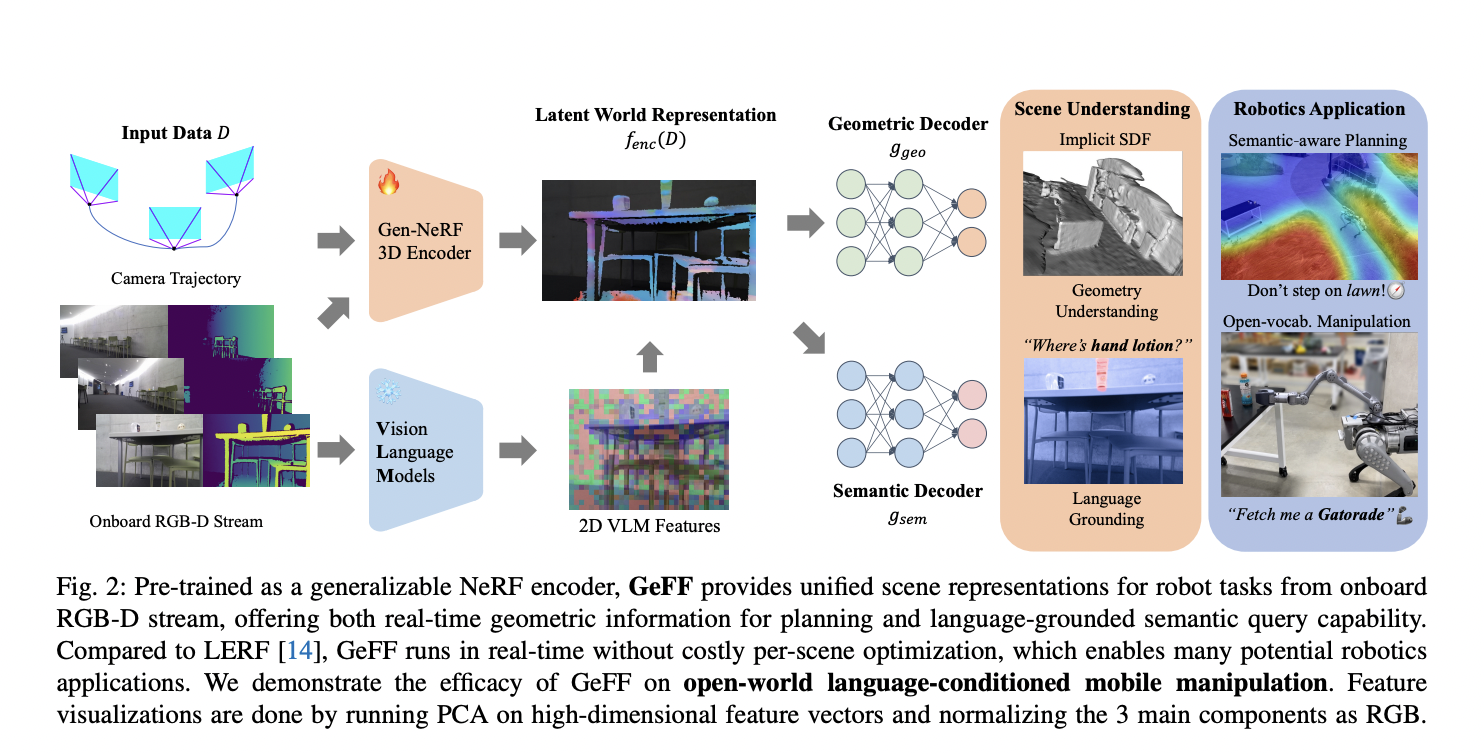
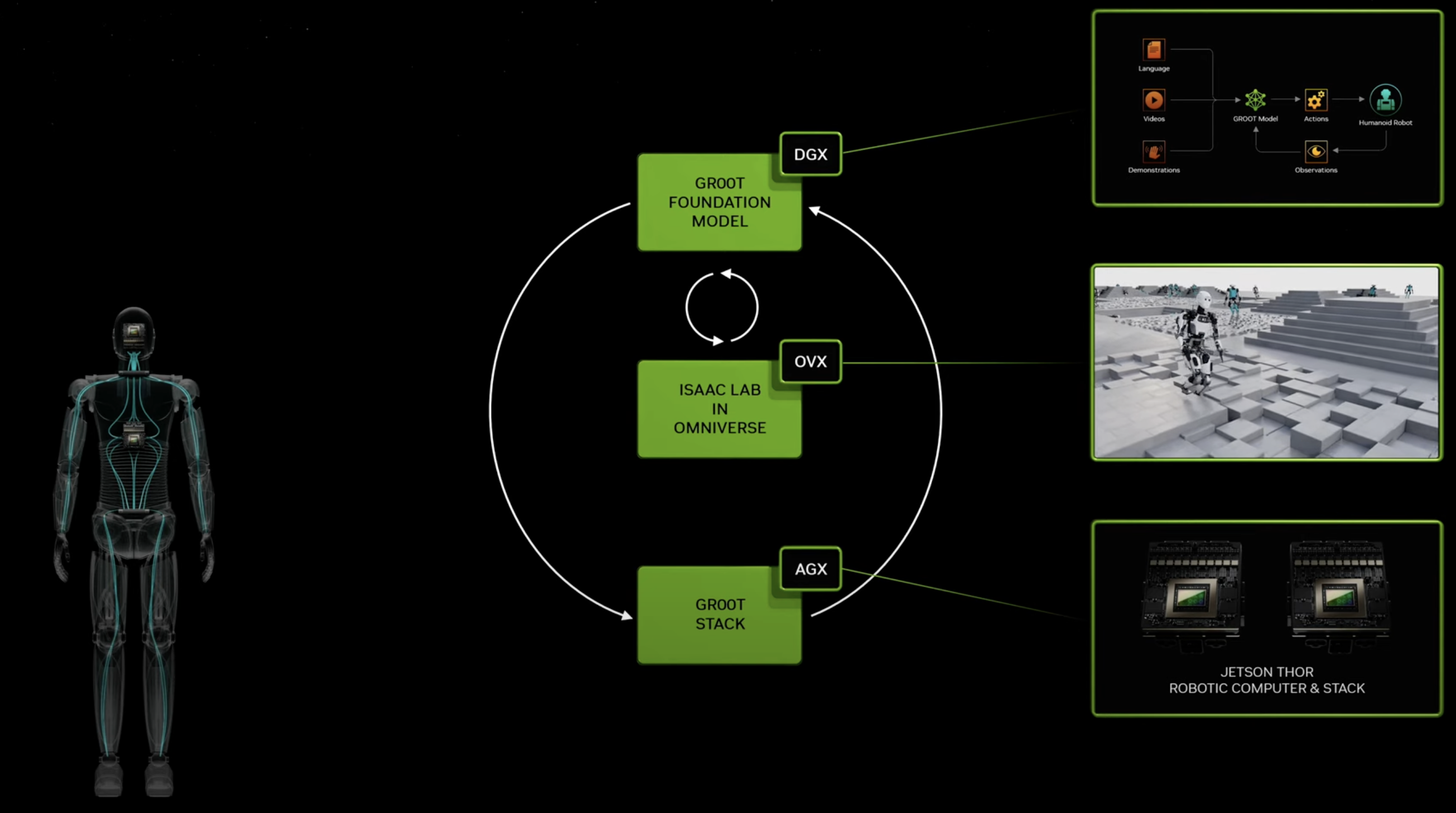
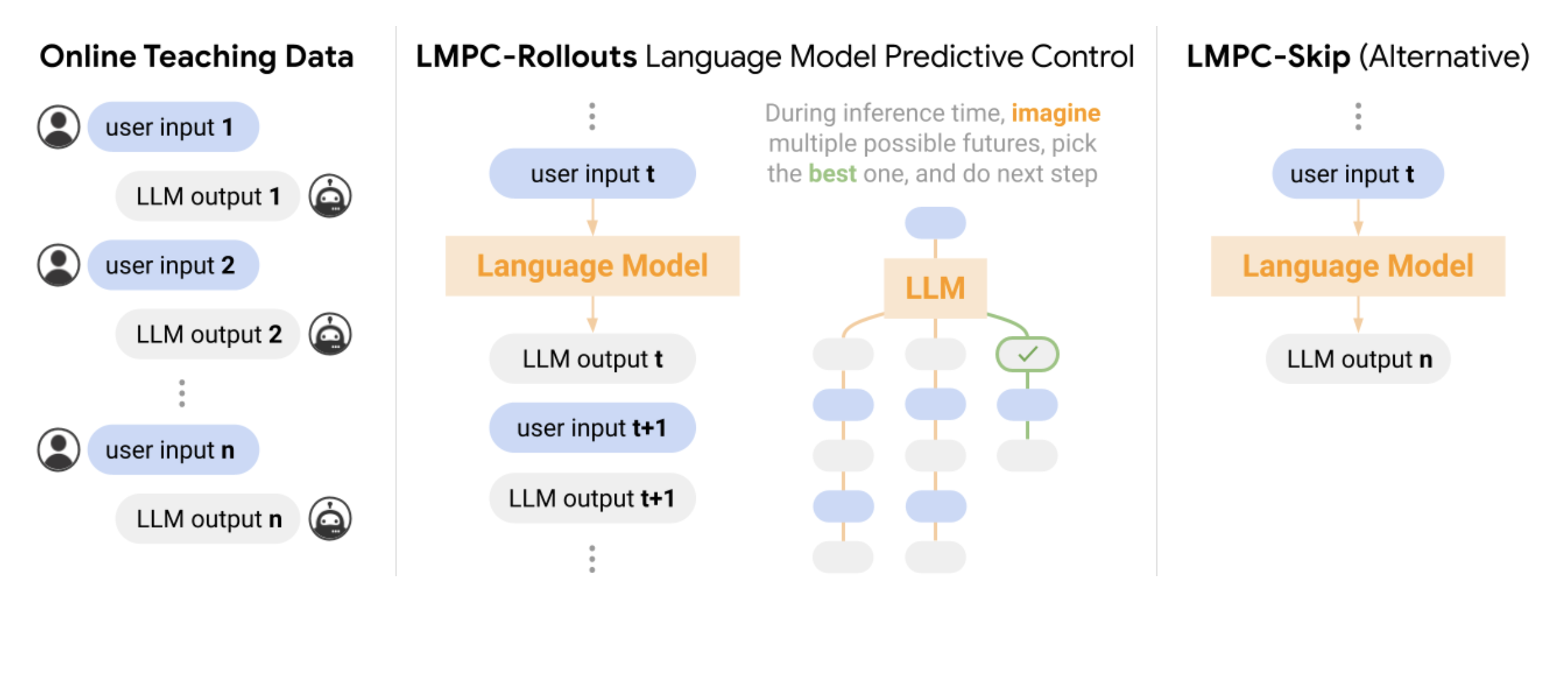
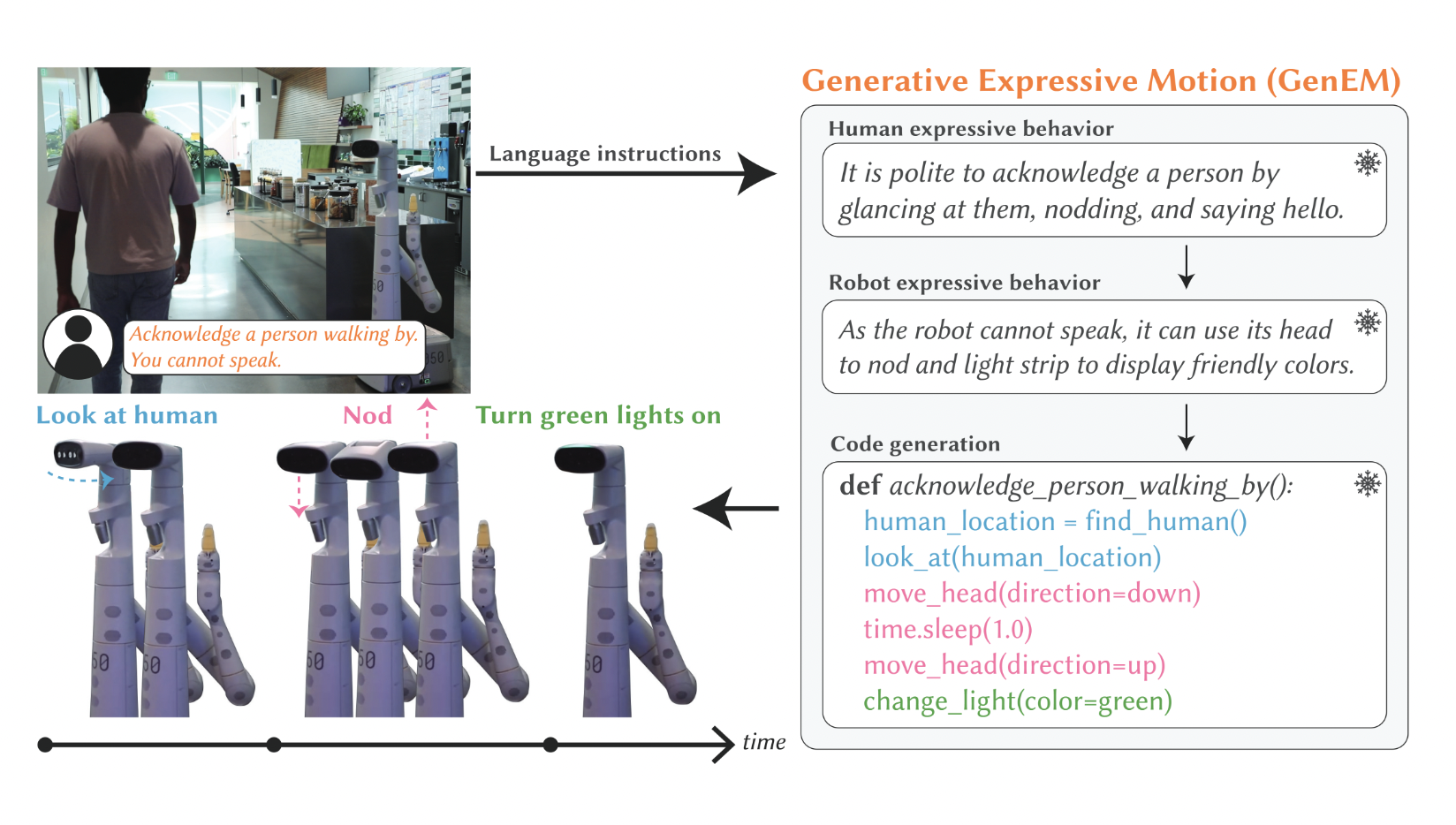
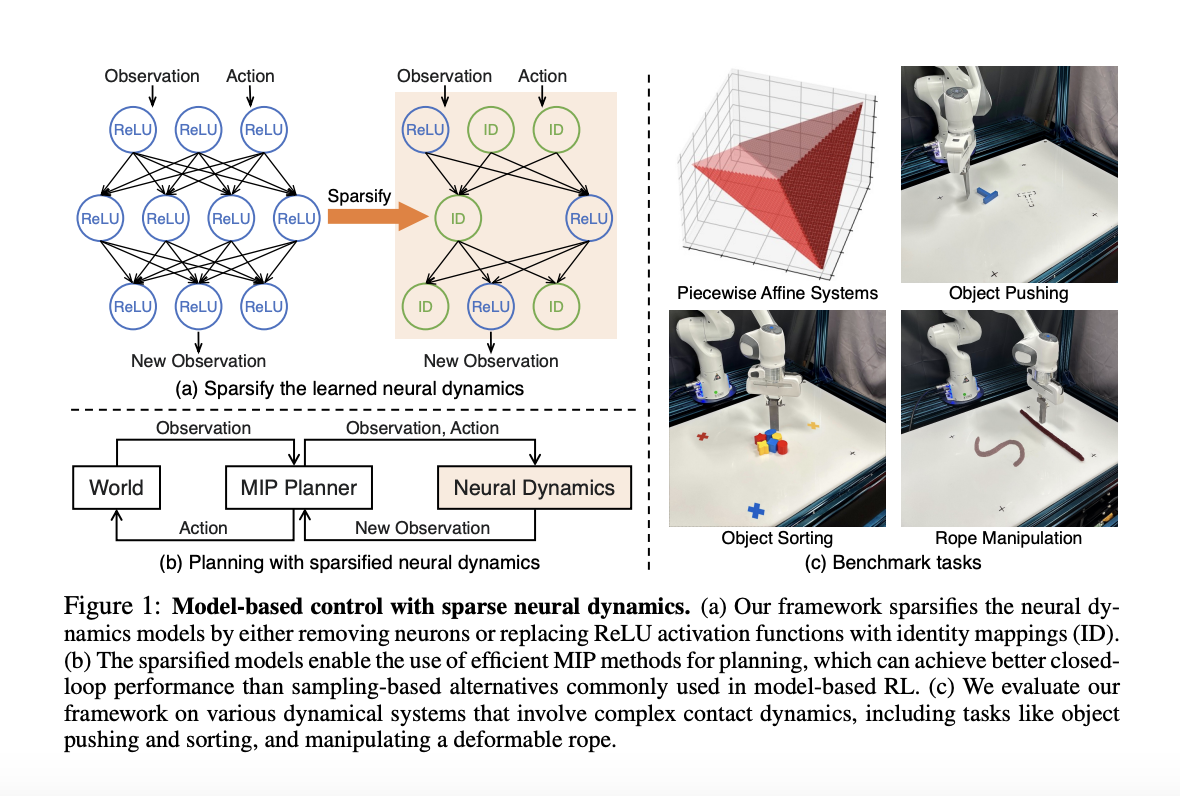
The exploration of artificial intelligence within dynamic 3D environments has emerged as a critical area of research, aiming to bridge the gap between static AI applications and their real-world usability. Researchers at Google DeepMind have pioneered this realm, developing sophisticated agents capable of interpreting and acting on complex instructions within various simulated settings. This new…