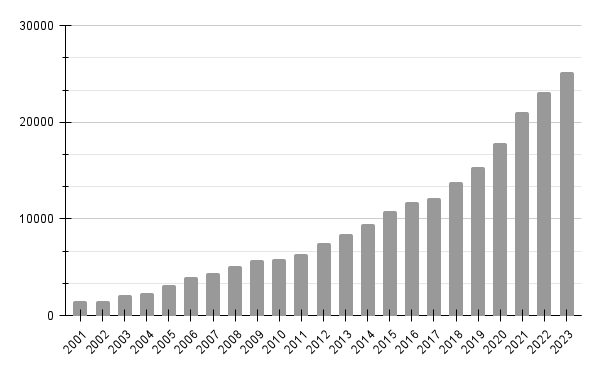
Choosing between frequentist and Bayesian approaches is the great debate of the last century, with a recent surge in Bayesian adoption in the sciences. Number of articles referring Bayesian statistics in sciencedirect.com (April 2024) — Graph by the authorWhat’s the difference? The philosophical difference is actually quite subtle, where some propose that the great bayesian…