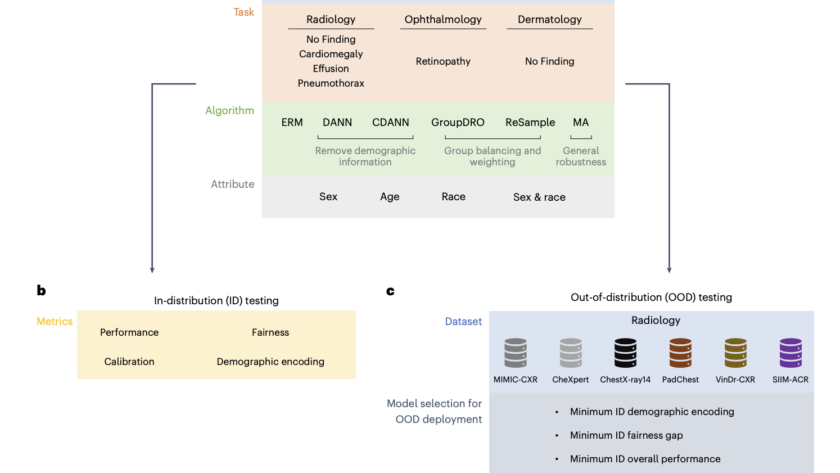
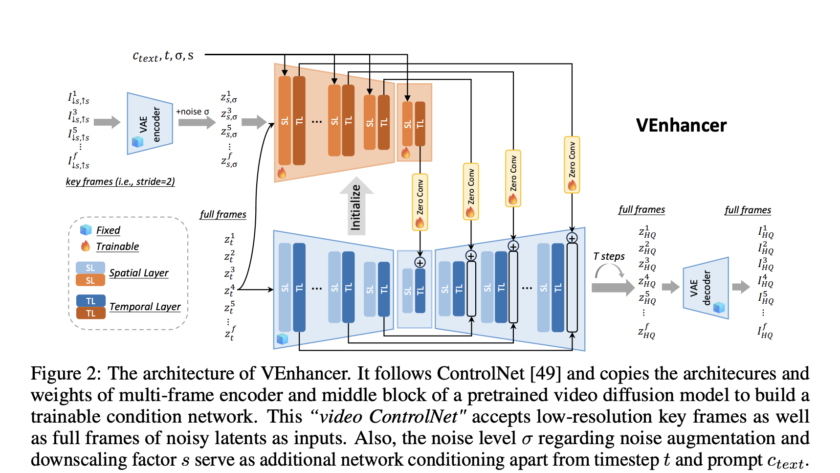
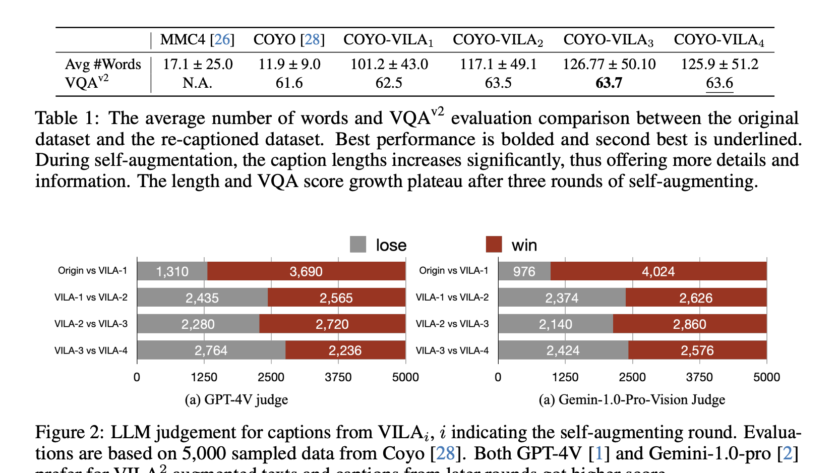
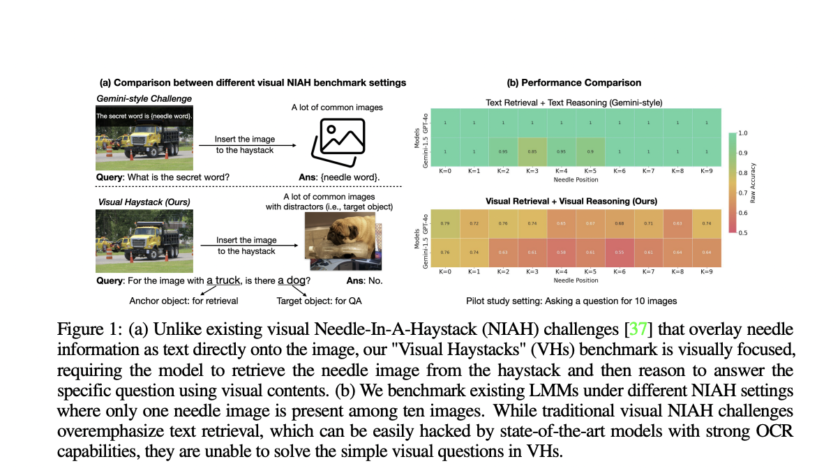
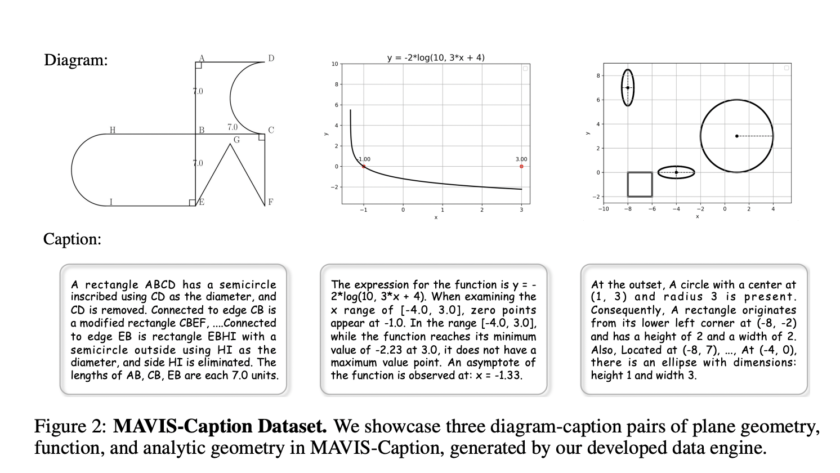
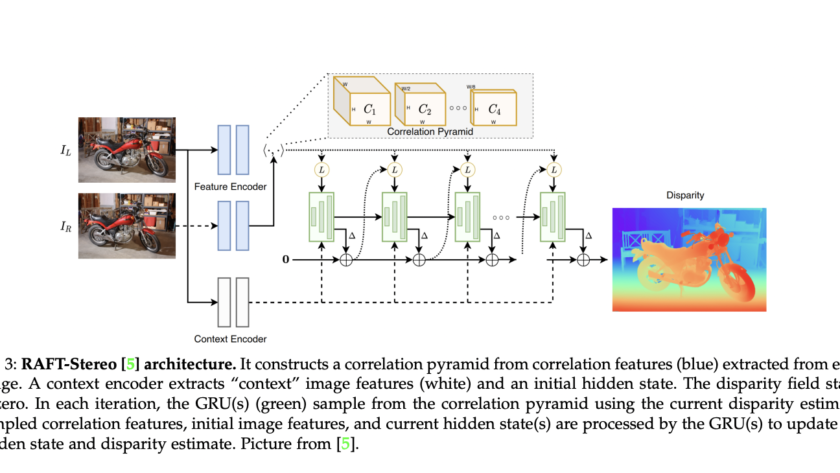
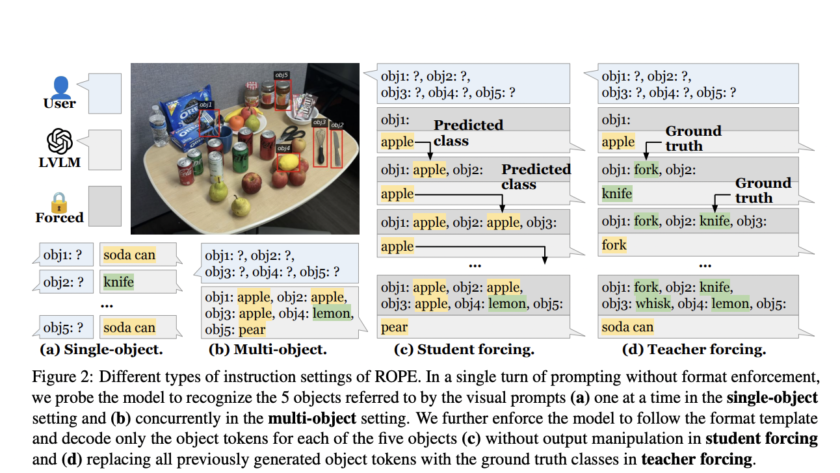
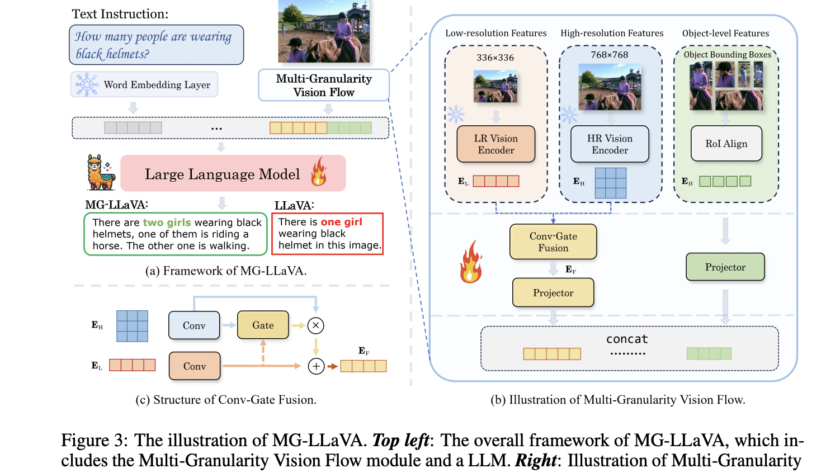
As AI models become more integrated into clinical practice, assessing their performance and potential biases towards different demographic groups is crucial. Deep learning has achieved remarkable success in medical imaging tasks, but research shows these models often inherit biases from the data, leading to disparities in performance across various subgroups. For example, chest X-ray classifiers…