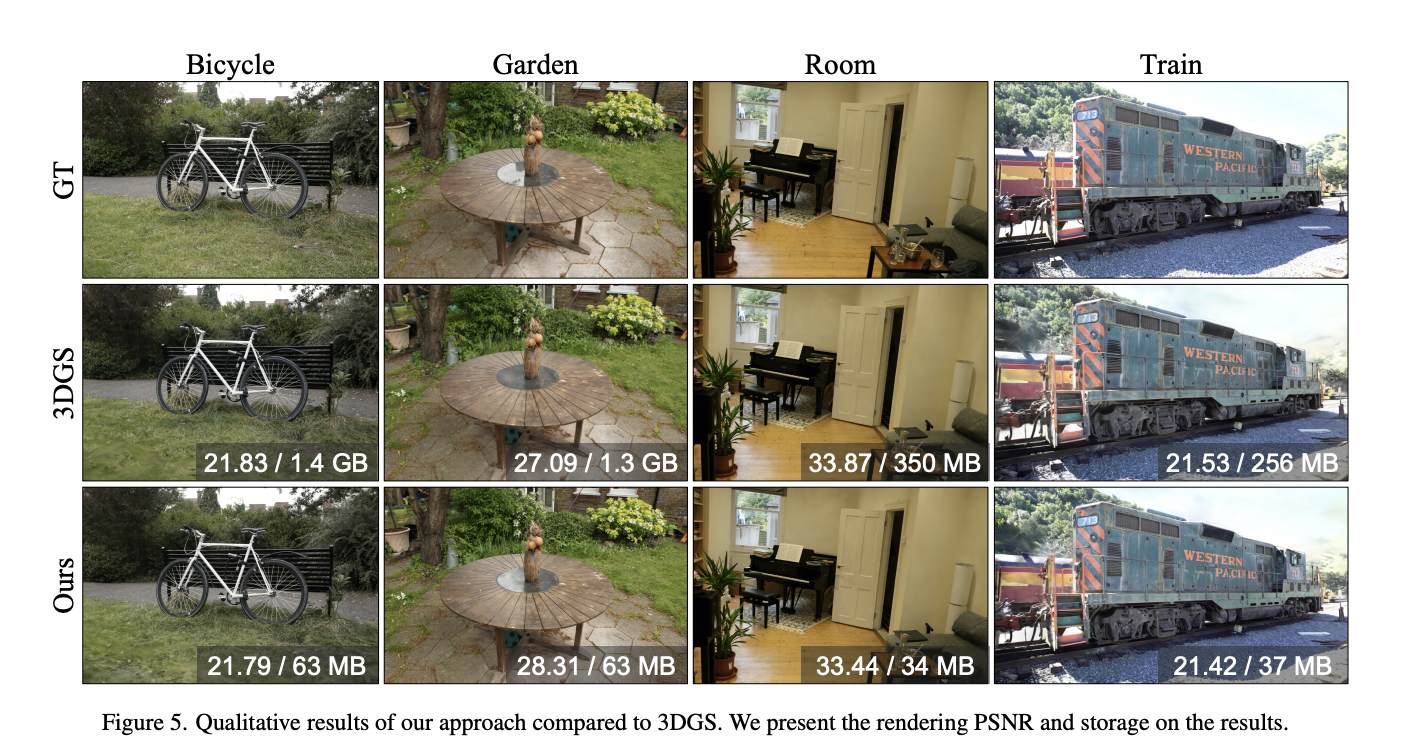
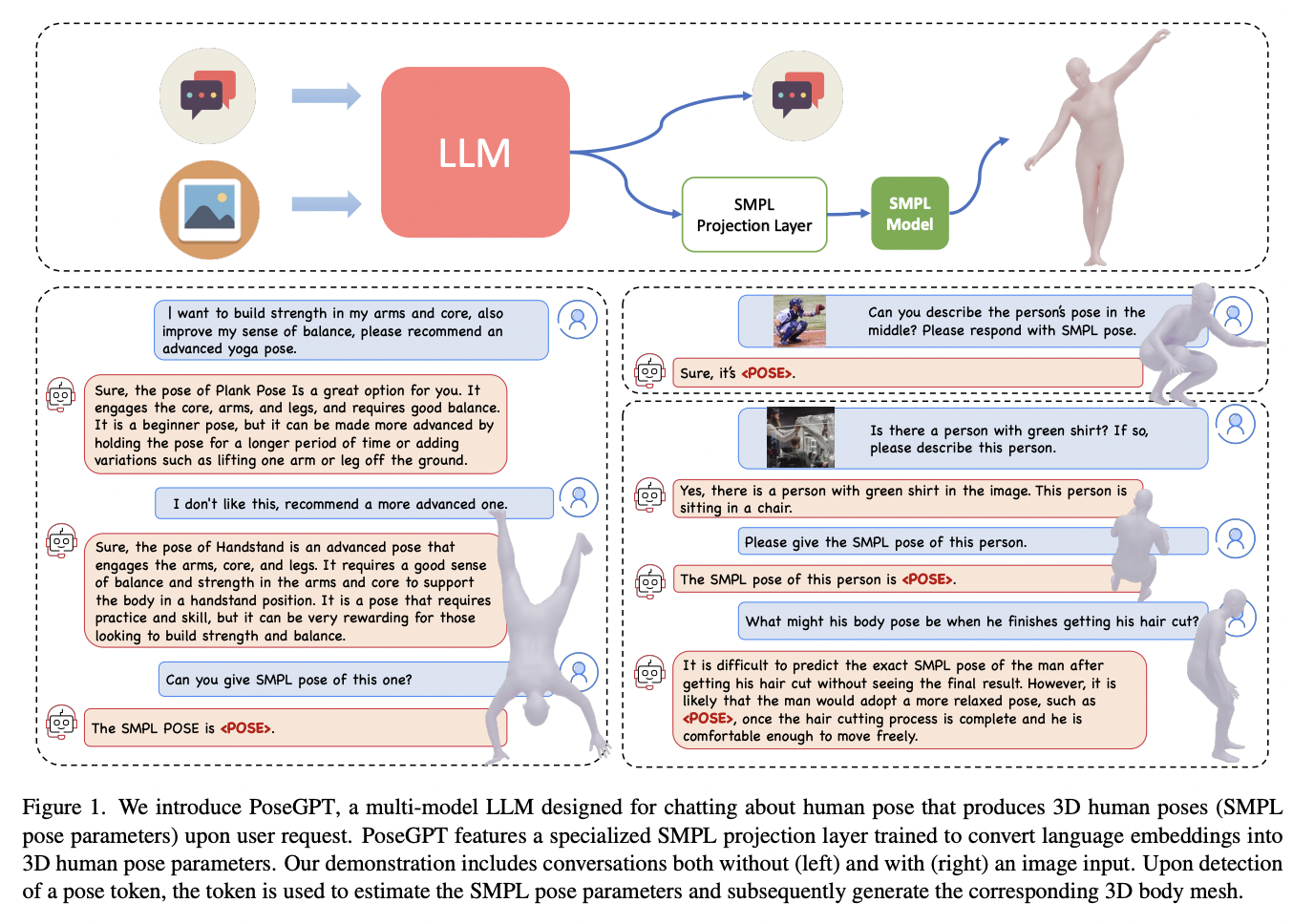
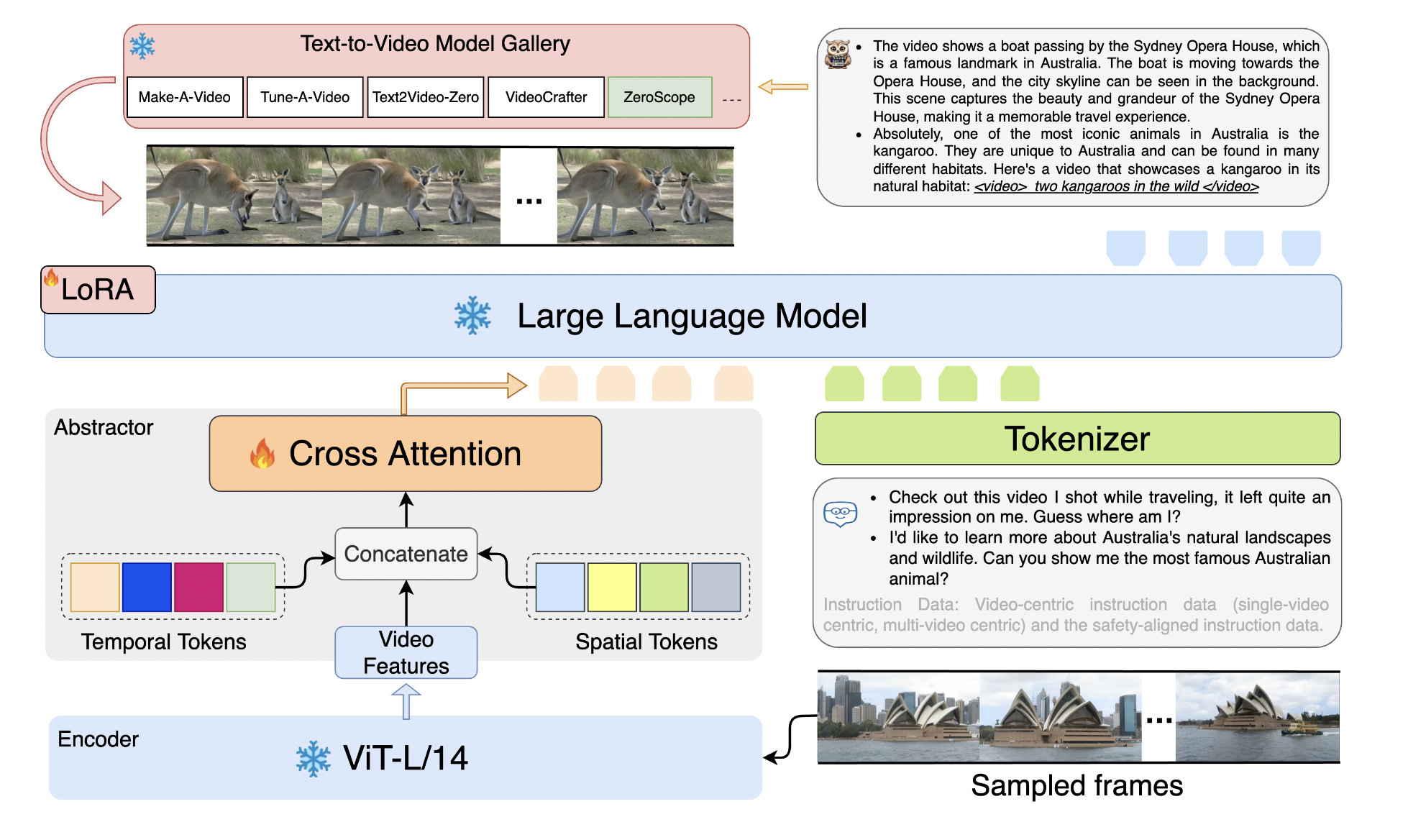
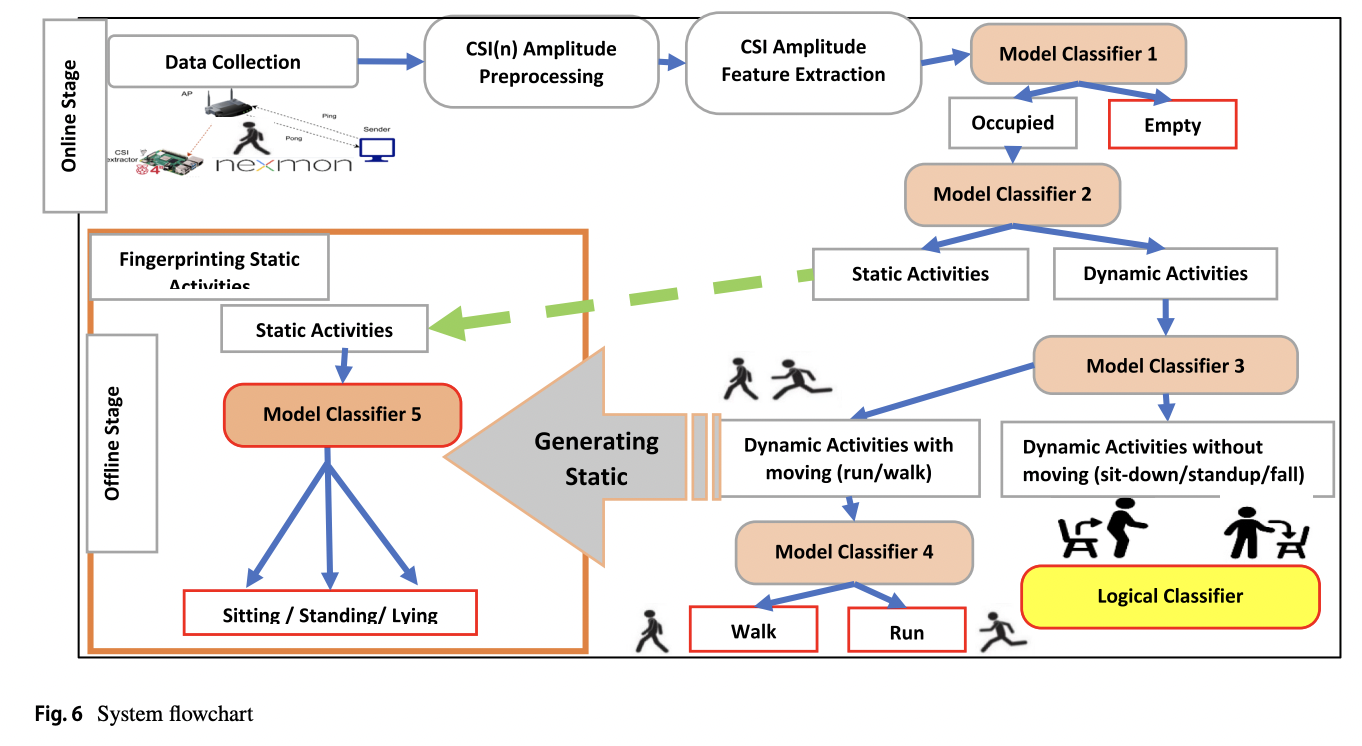
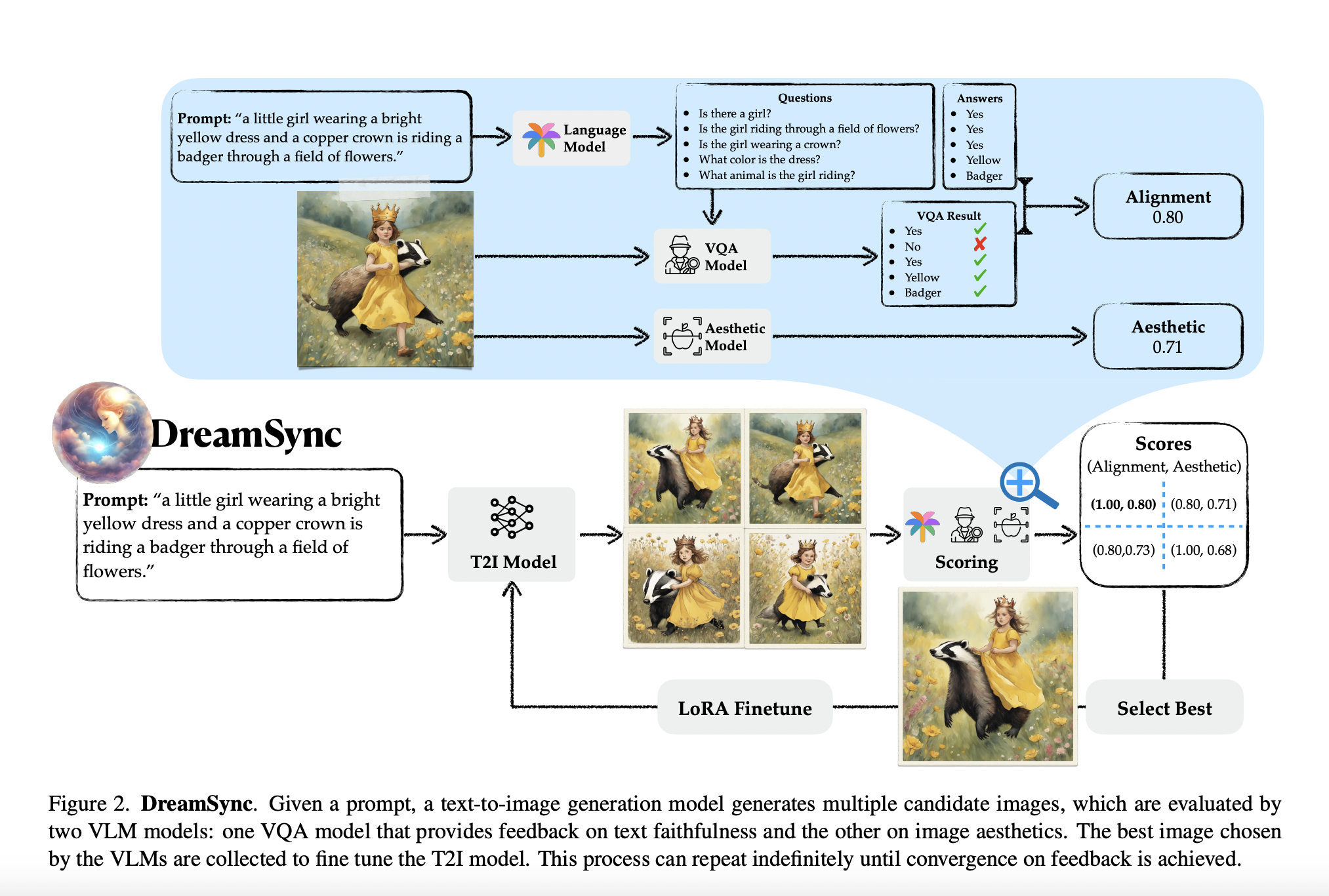
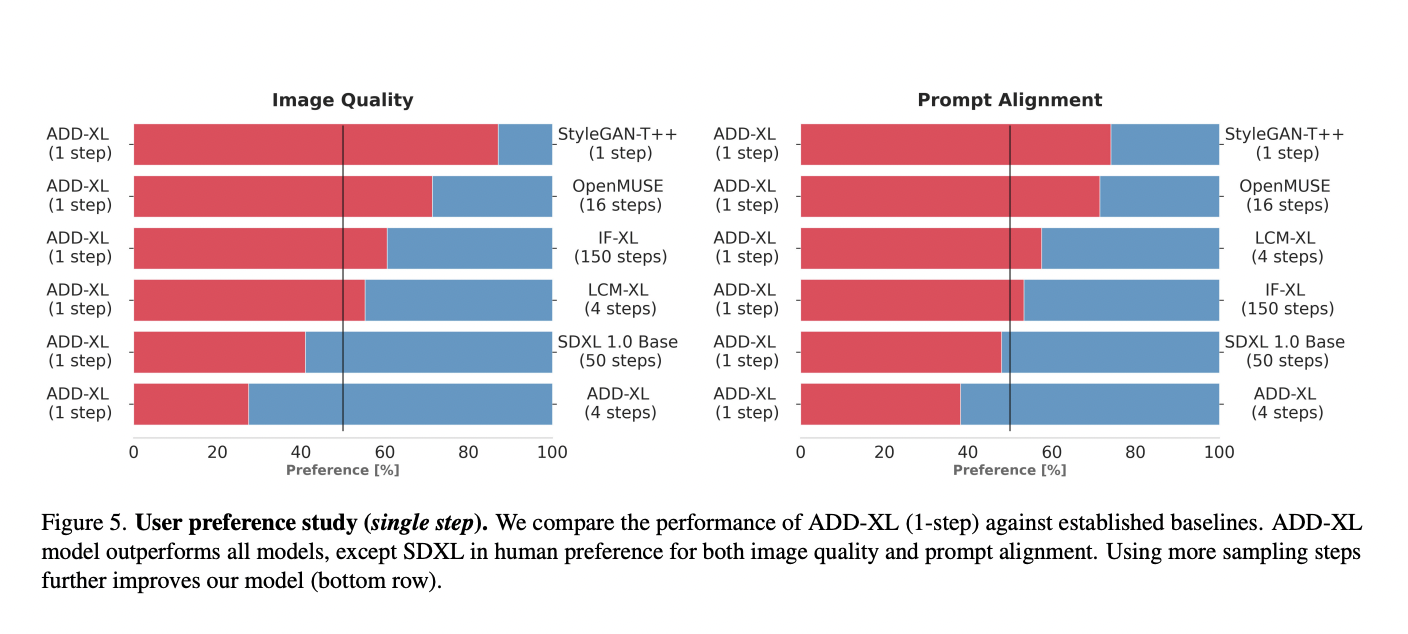
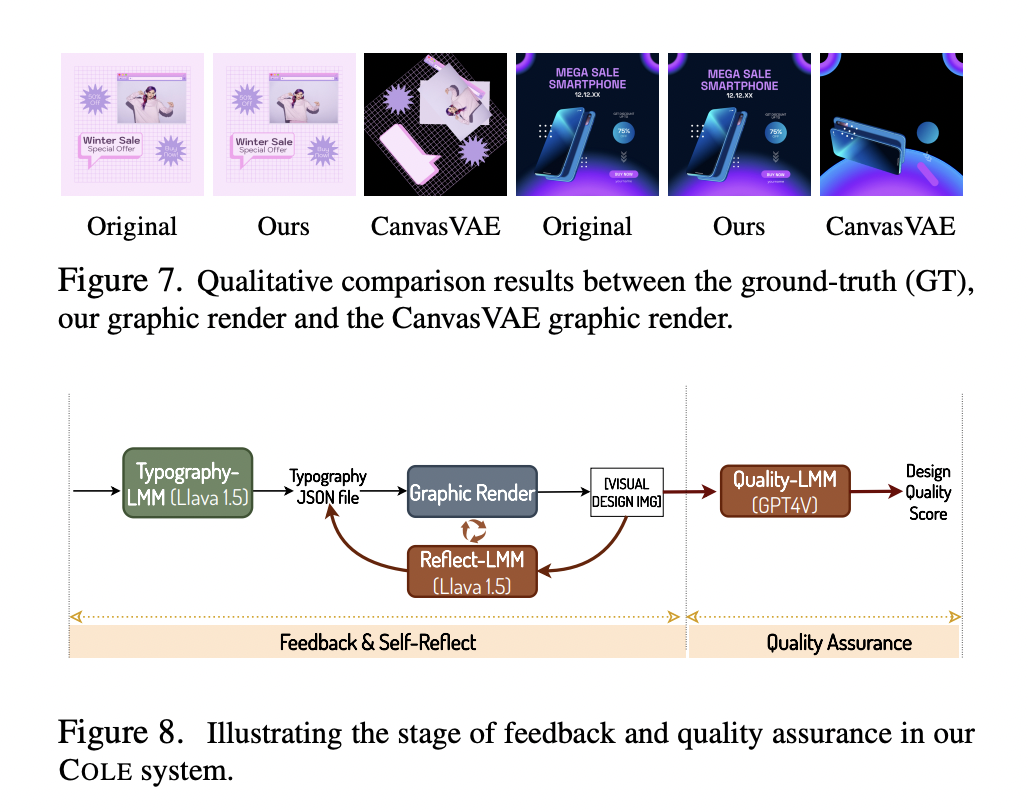
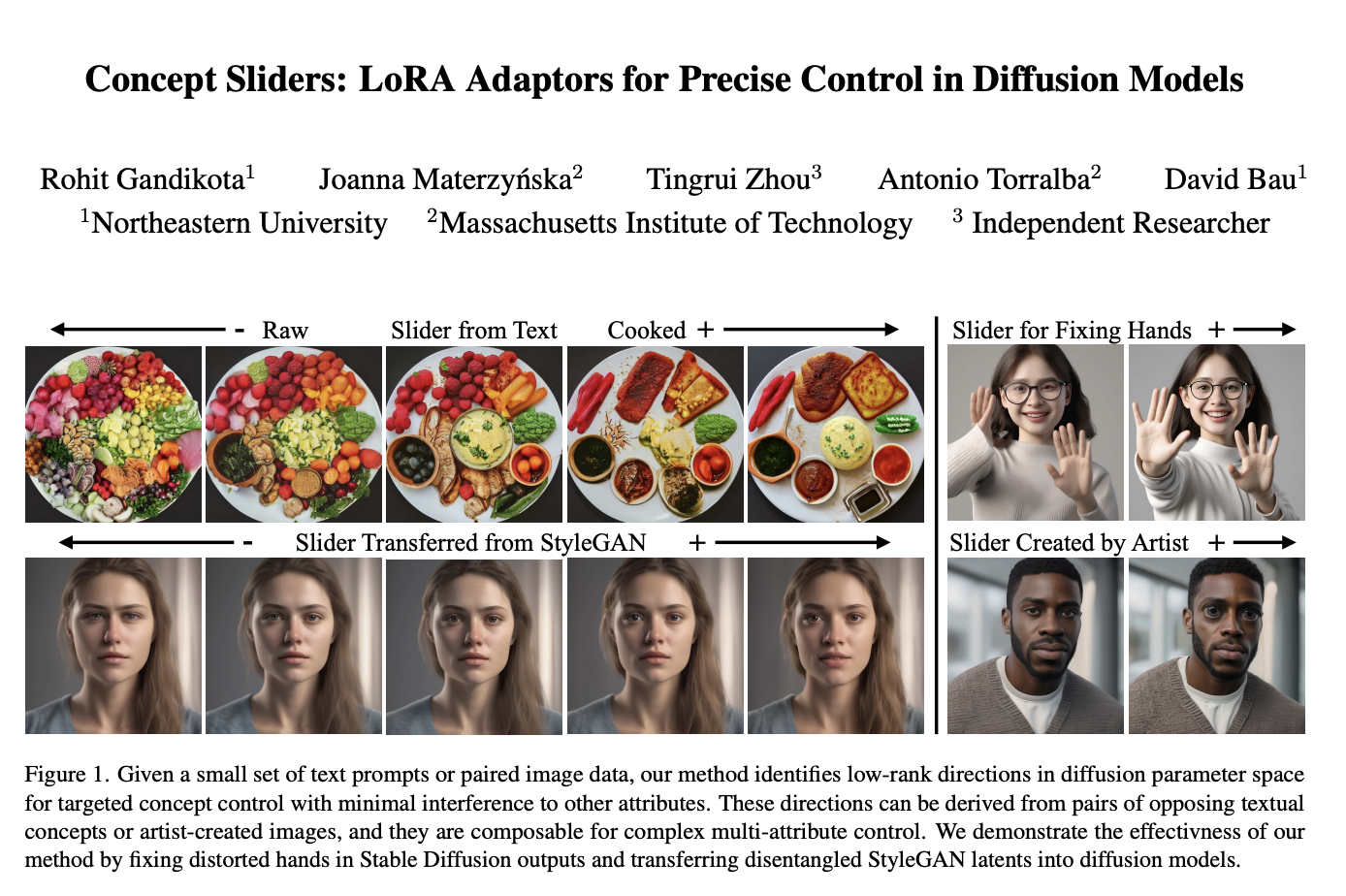
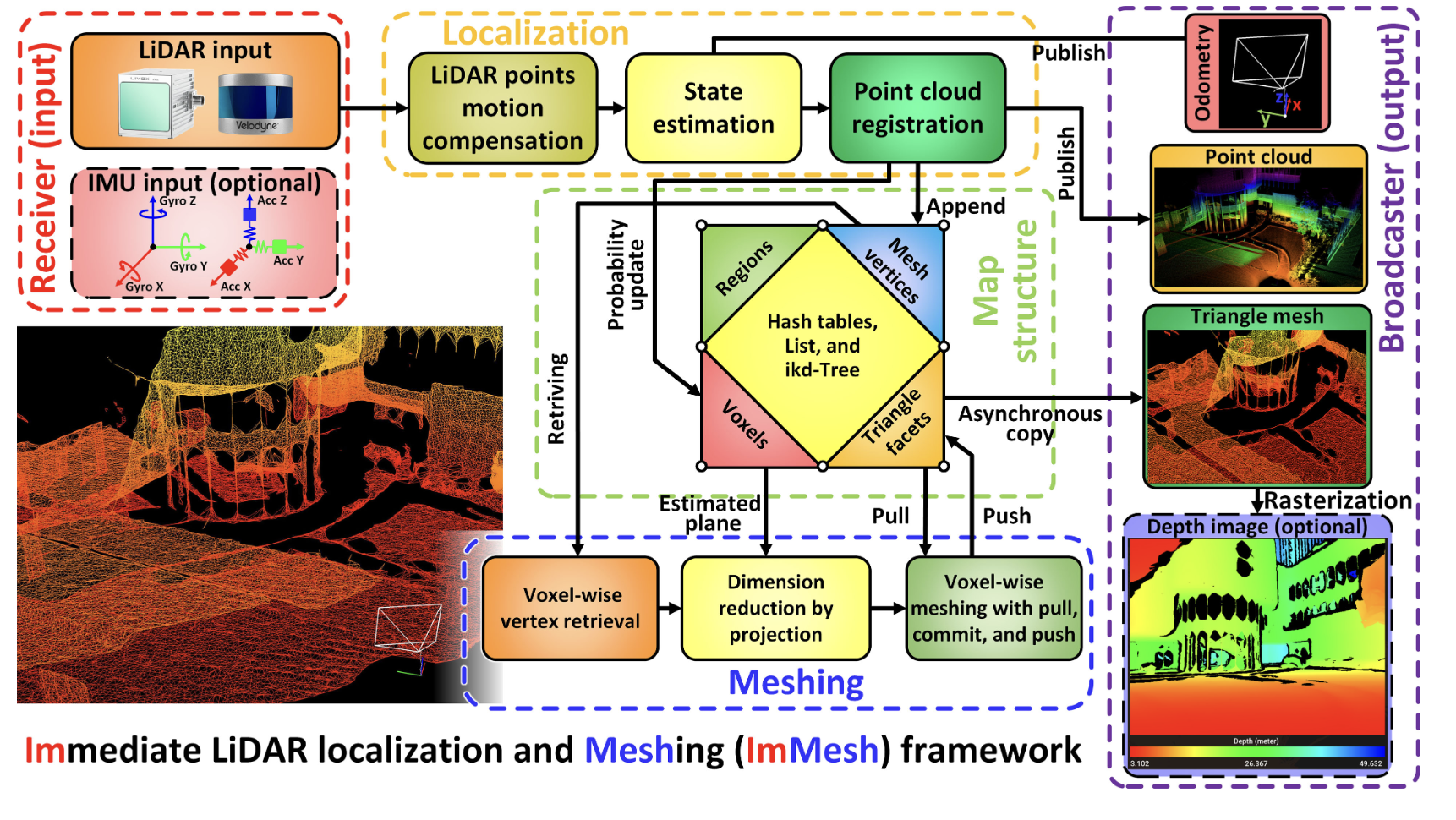
Human posture is crucial in overall health, well-being, and various aspects of life. It encompasses the alignment and positioning of the body while sitting, standing, or lying down. Good posture supports the optimal alignment of muscles, joints, and ligaments, reducing the risk of muscular imbalances, joint pain, and overuse injuries. It helps distribute the body’s…