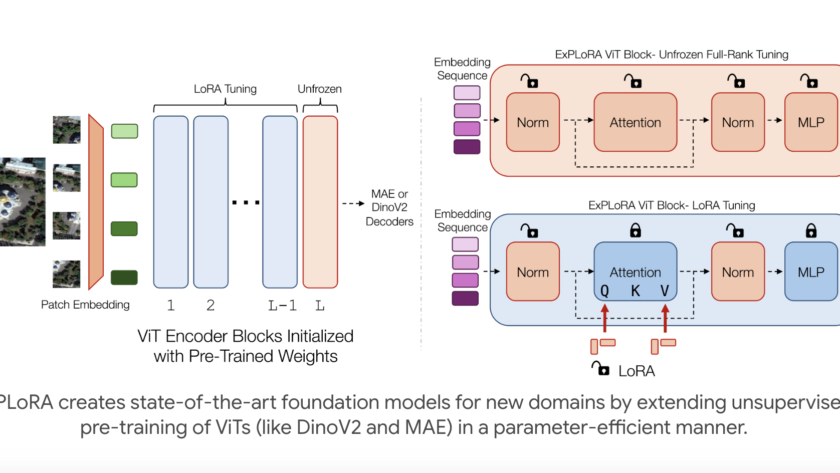
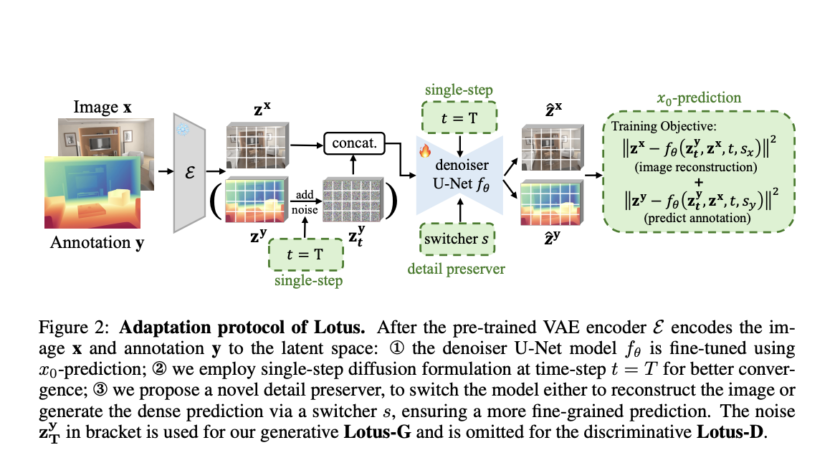
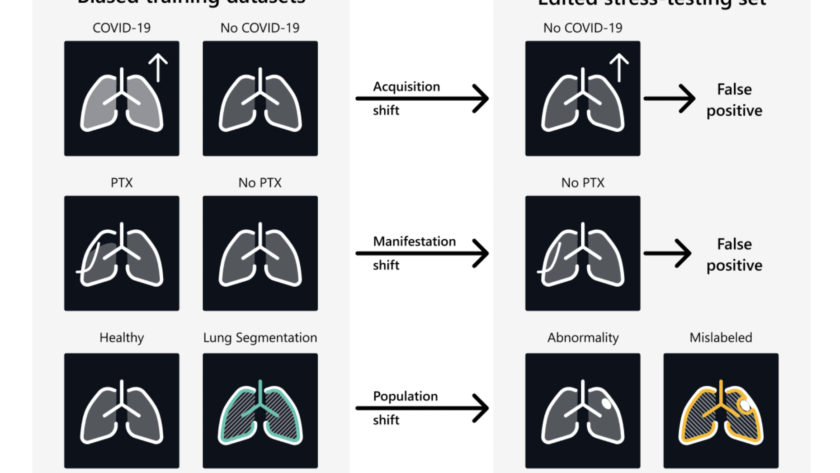
Computer vision is rapidly transforming industries by enabling machines to interpret and make decisions based on visual data. From autonomous vehicles to medical imaging, its applications are vast and growing. Learning computer vision is essential as it equips you with the skills to develop innovative solutions in areas like automation, robotics, and AI-driven analytics, driving…