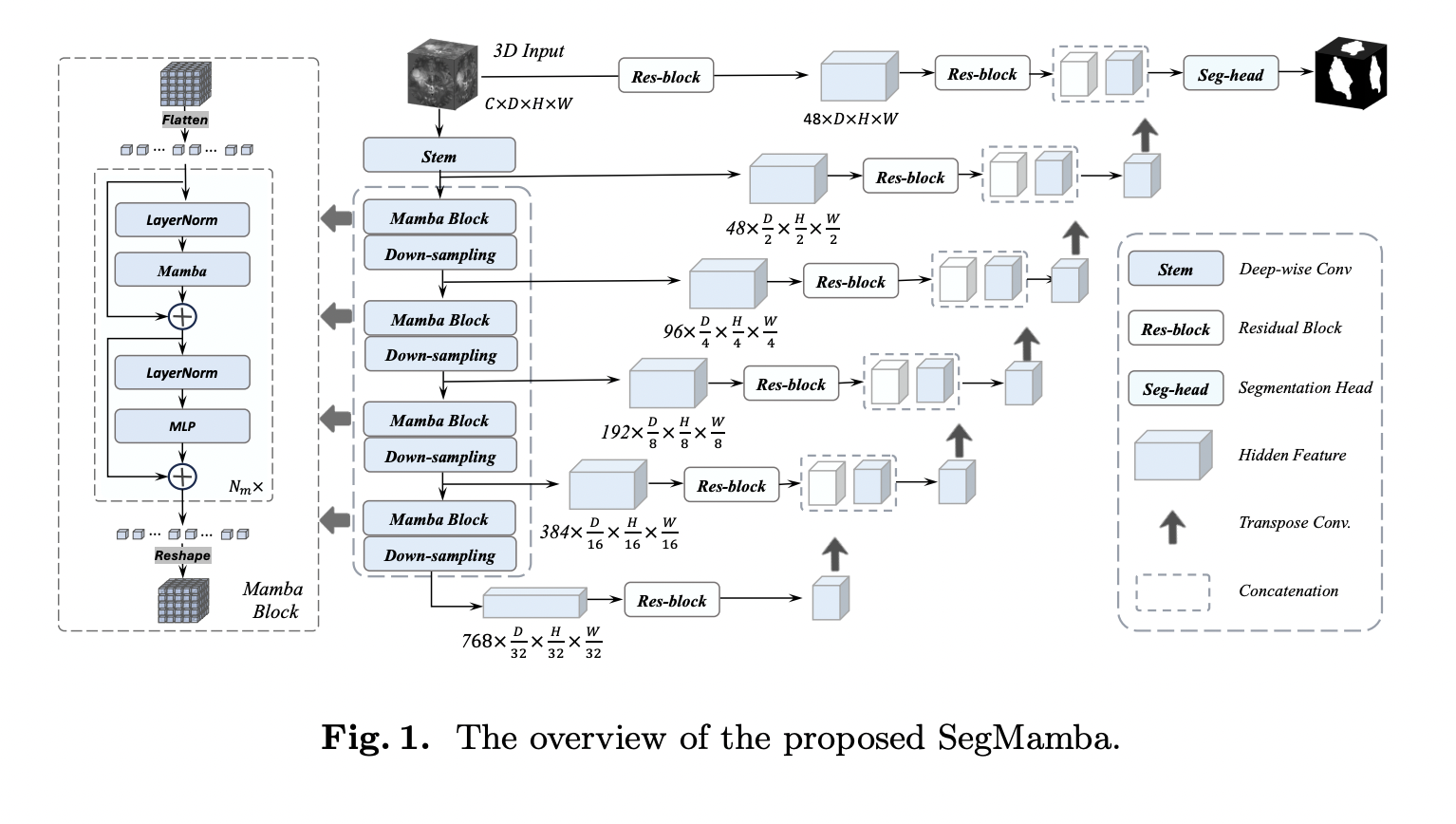
Enhancing the receptive field of models is crucial for effective 3D medical image segmentation. Traditional convolutional neural networks (CNNs) often struggle to capture global information from high-resolution 3D medical images. One proposed solution is the utilization of depth-wise convolution with larger kernel sizes to capture a wider range of features. However, CNN-based approaches need help…