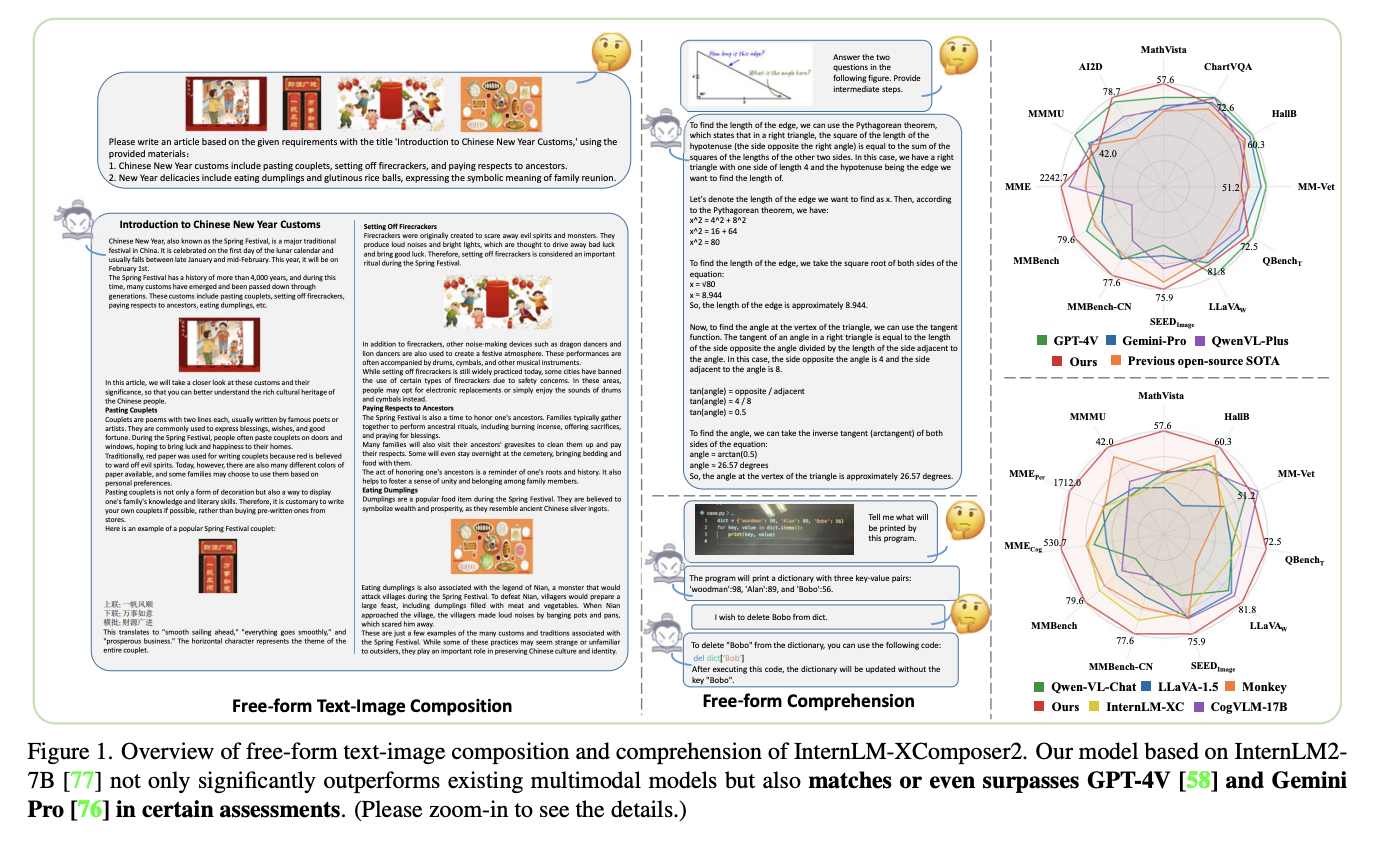
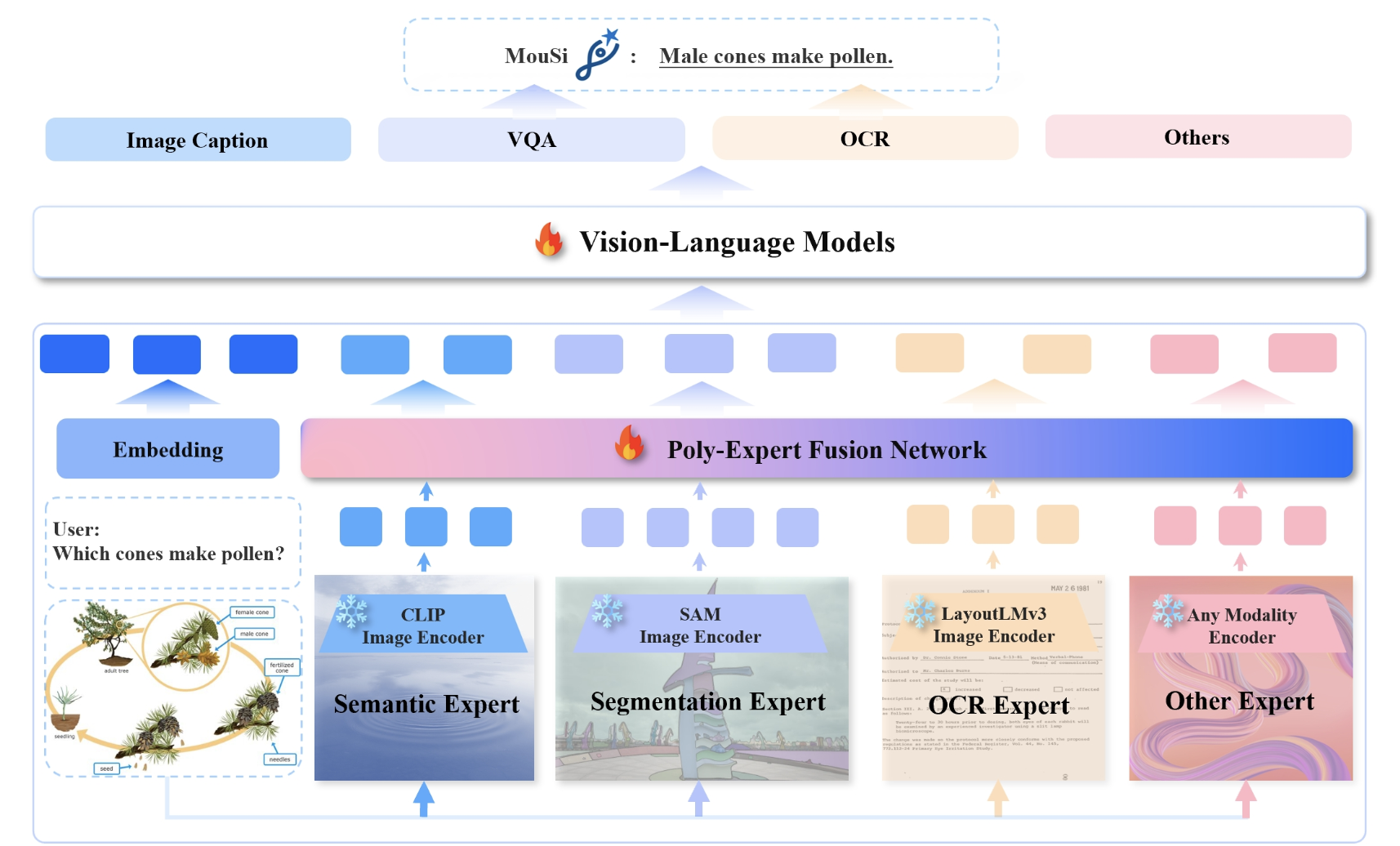
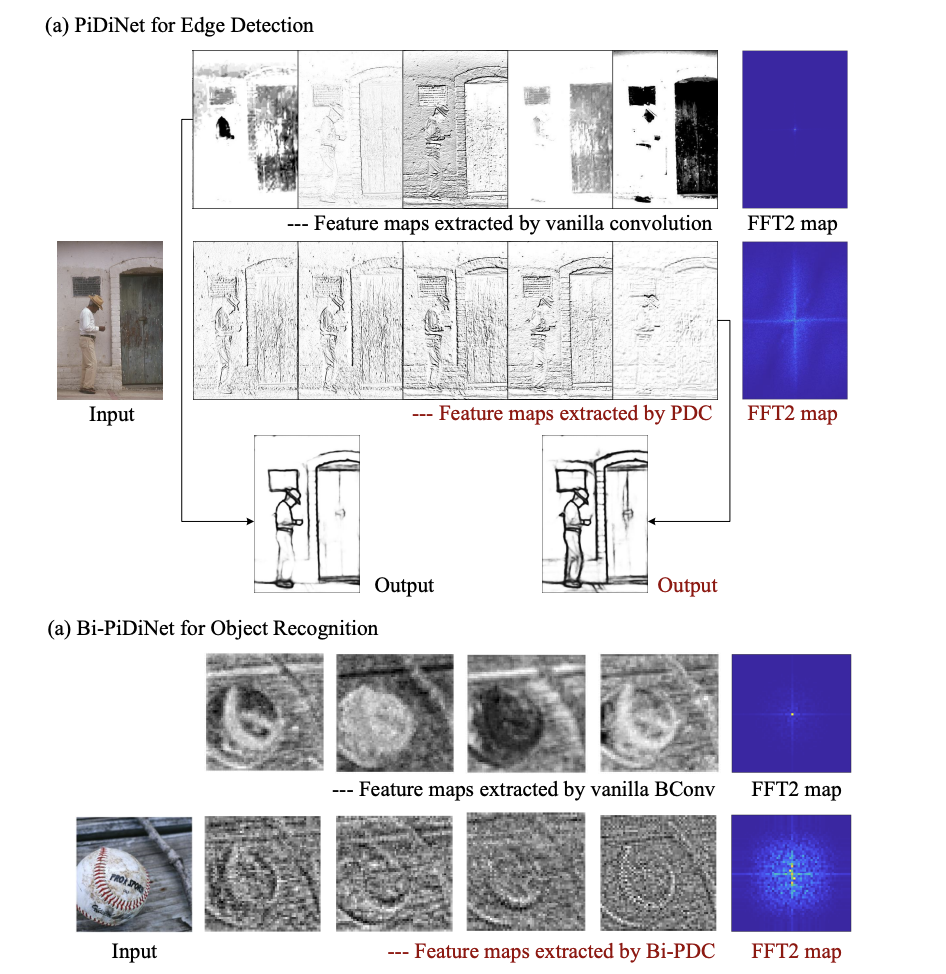
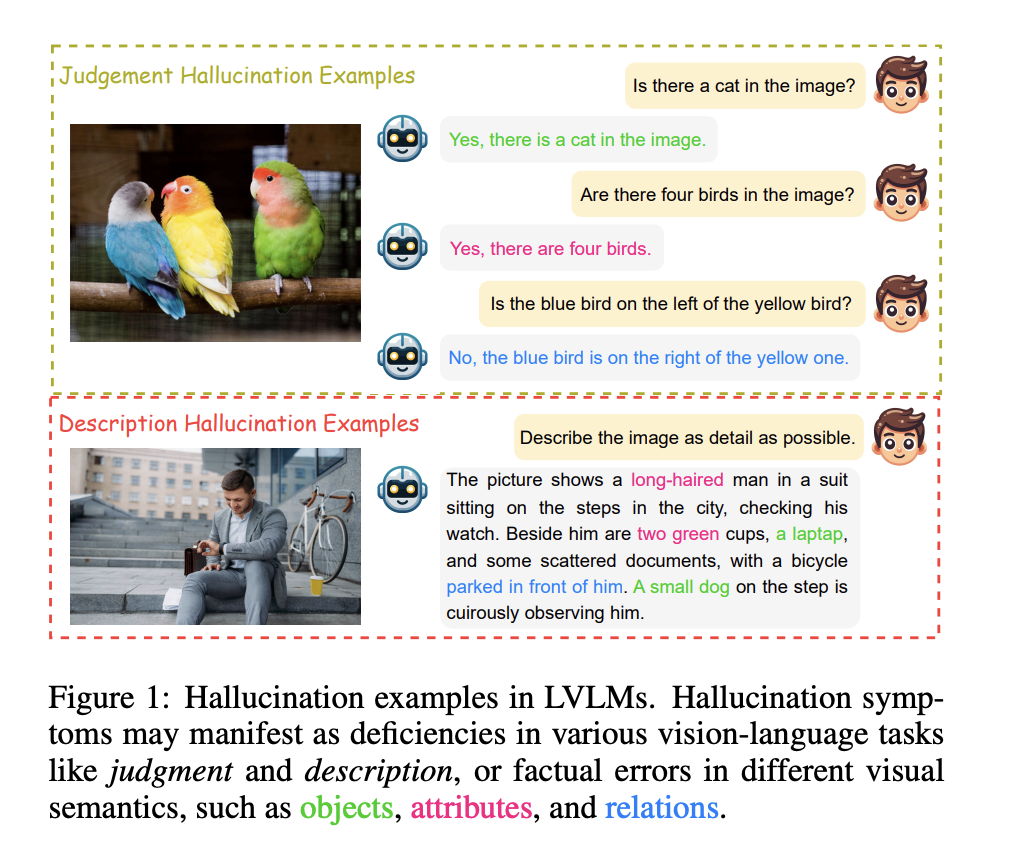
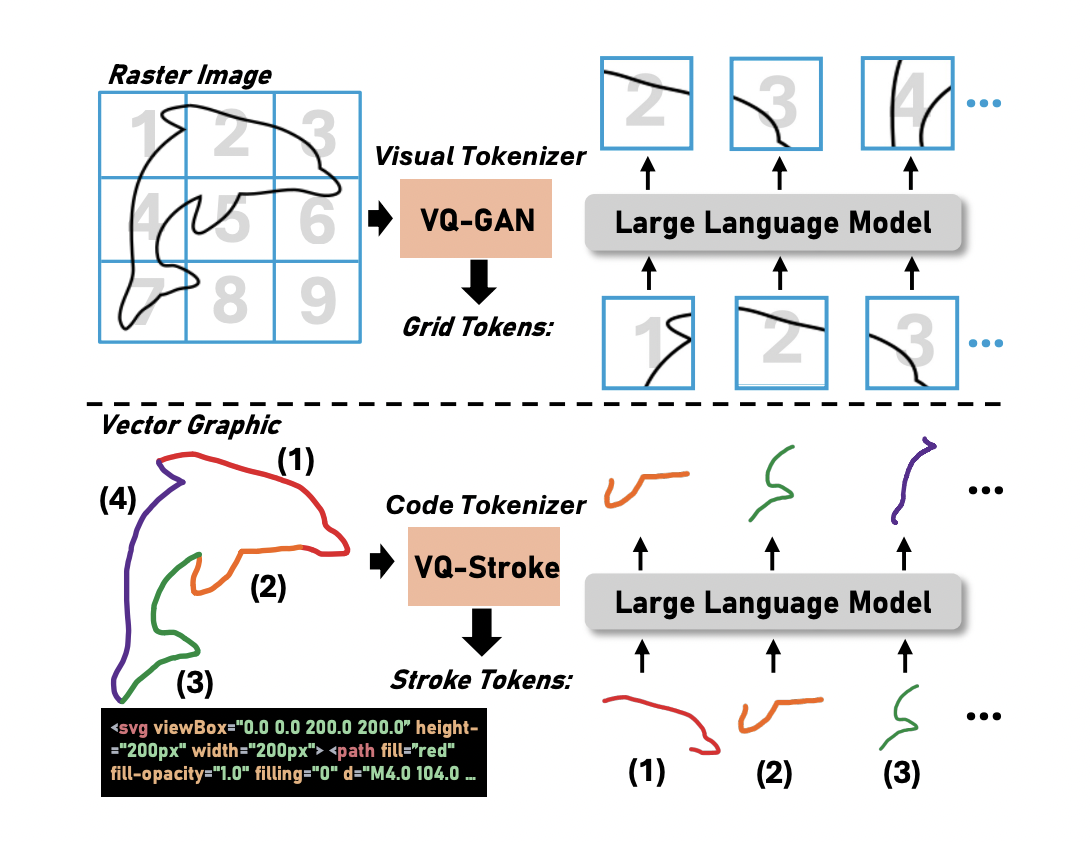
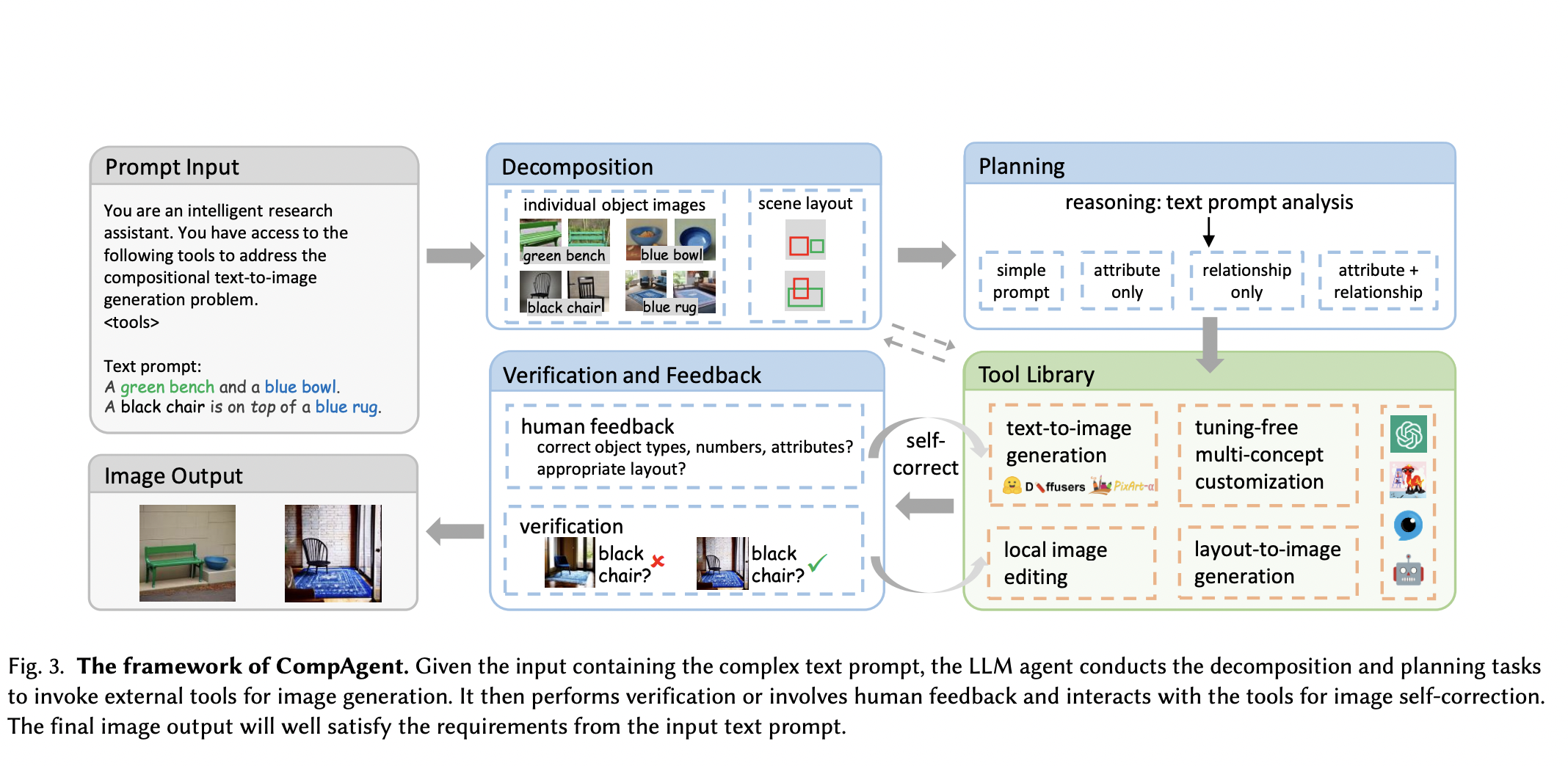
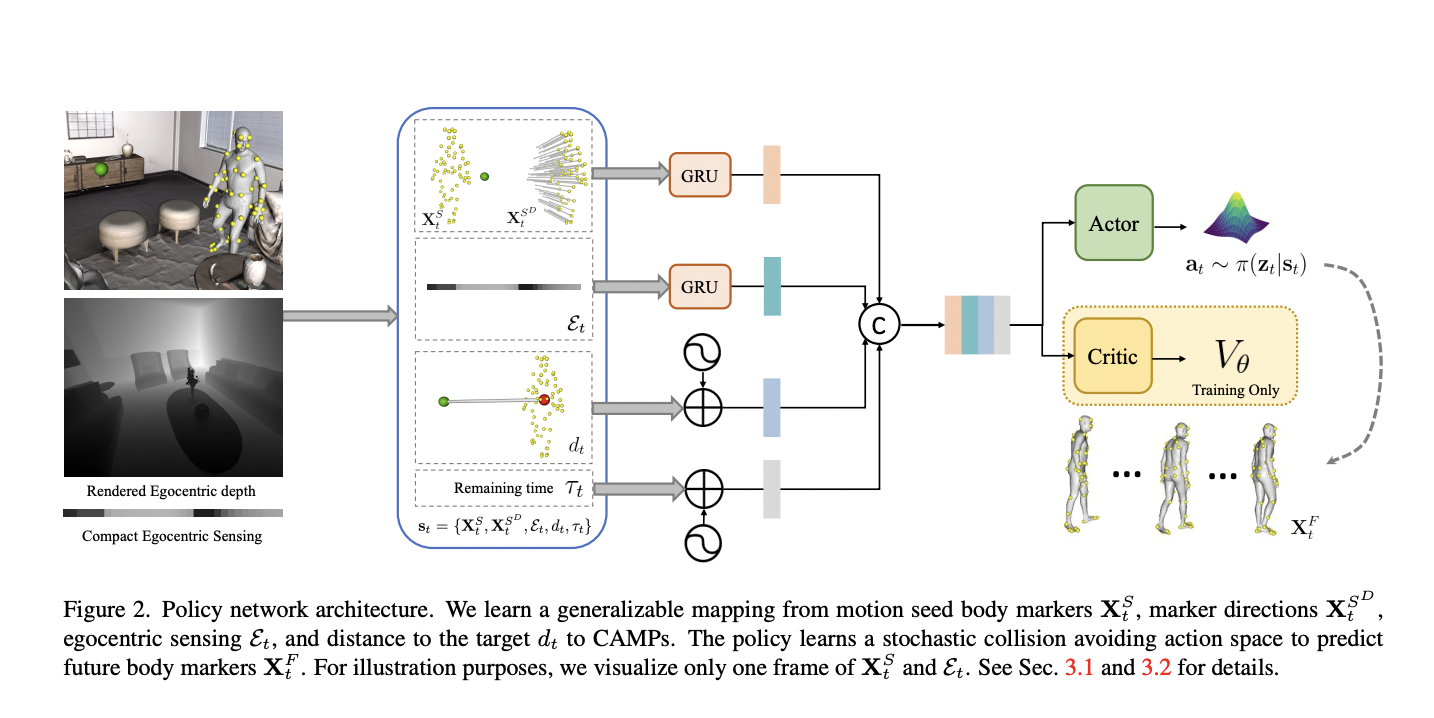
The advancement of AI has led to remarkable strides in understanding and generating content that bridges the gap between text and imagery. A particularly challenging aspect of this interdisciplinary field involves seamlessly integrating visual content with textual narratives to create cohesive and meaningful multi-modal outputs. This challenge is compounded by the need for systems that…