Over the years, the auditing landscape has undergone remarkable transformations, and among the most significant advancements has been the advent of audit automation software solutions. Research shows that adopting audit automation tools can significantly reduce costs and save time, and there has been a shift towards increased technology utilization.
The advent of AI tools has pushed this shift further. According to TechNavio, the audit software market is poised for substantial growth, with an estimated Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 13.36% anticipated between 2022 and 2027. The market is expected to witness a significant increase, amounting to USD 999.24 million.
In this article, we’ll discuss the fundamentals of audit automation, its benefits, and the top tools available. We’ll also provide practical, actionable insights that you can implement immediately in your audit workflow to enhance efficiency, accuracy, and overall performance.
What is audit automation software?
Audit automation software refers to the use of advanced AI software and cloud-based data to streamline the auditing process. It involves automating repetitive and routine audit procedures, such as data collection, analysis, risk assessment, and testing of internal controls.
Before we get into the details of the audit automation, let’s quickly recap the auditing basics.
Auditing is the process of examining an organization’s financial records, operations, and internal controls to ensure compliance with laws, regulations, and industry standards. The goal is to provide stakeholders with an independent, objective assessment of the organization’s financial health and risk management practices.
Traditionally, audit management involved manual processes, such as:
- Planning: Auditors identify risk areas, develop an audit plan, and assign resources.
- Fieldwork: Auditors collect and analyze data, conduct interviews, and test internal controls.
- Reporting: Auditors document their findings, prepare audit reports, and communicate results to stakeholders.
- Follow-up: Auditors ensure that recommendations are implemented and issues are resolved.
Throughout this process, auditors would rely on inefficient tools, such as spreadsheets, word processing software, and email, to manage their work. These tools lack the functionality and integration necessary to streamline the audit process, leading to inefficiencies and potential errors.
Modern audit software addresses these challenges by leveraging advanced technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), natural language processing (NLP), data integration tools, predictive models, and data analytics. These technologies enable auditors to reduce audit costs, speed up audit cycles, improve audit quality, and enhance risk identification. Automating the audit process also frees auditors to provide more strategic, value-added insights to the organization.
Audit management software significantly streamlines workflows and conserves resources required for compliance, making it an essential tool for organizations. With its capacity to deliver valuable insights and effectively mitigate risks, audit automation is a powerful ally in enhancing efficiency, making your business more productive, and driving success.
How does audit automation work?
As we’ve seen, modern audit software leverages cognitive capabilities to streamline and optimize the auditing process. But how exactly does it work? Let’s take a closer look at the step-by-step process of audit automation.

- Data collection: The first step of collecting financial data from various sources, including bank statements, invoices, payment receipts, operational databases, spreadsheets, and other relevant repositories, is the most time-consuming of the entire operation. Using audit automation software to capture and categorize financial data automatically is the first step of audit automation.
- Data integration: The collected data is then integrated and consolidated into a centralized platform. Automated auditing tools can handle diverse data formats, allowing auditors to access and analyze information from different sources seamlessly.
- Data analytics: AI-powered data analytics tools are employed to analyze the consolidated financial data. These audit tools can process large volumes of information and perform complex calculations to identify patterns, trends, and anomalies in the financial data that help overcome roadblocks in the auditing process.
- Risk assessment: Audit management software helps auditors assess risks more effectively by identifying potential red flags and areas of concern within the data. It enables a comprehensive and targeted risk assessment process, ensuring no potential issues are overlooked.
- Continuous monitoring: Some audit automation solutions offer continuous monitoring capabilities, enabling real-time tracking of key performance indicators and potential risk indicators. This proactive approach ensures that auditors can promptly address emerging risks.
AI audit software empowers auditors to work more efficiently, accurately, and strategically. It enables them to focus on high-value tasks, such as analyzing complex transactions, interpreting qualitative information, and providing valuable insights to stakeholders while the software handles the repetitive and time-consuming aspects of the audit.
With a plethora of audit automation software tools available in the market, it can be overwhelming to choose the right one for your organization. To help you make an informed decision, we’ve compiled a list of the top 12 audit automation software tools, along with their key features, best-suited industries and use cases, pros, and cons.
1. SAP Audit Management
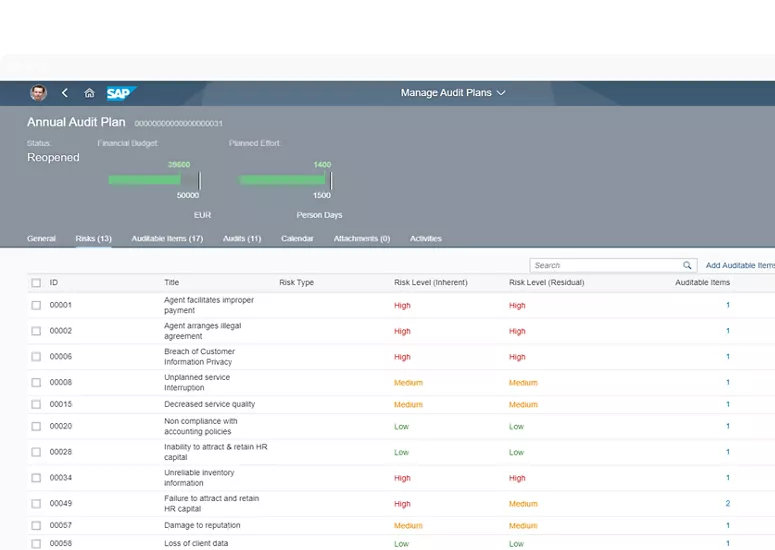
SAP Audit Management is a cutting-edge component of SAP ERP, designed to accelerate business growth and enhance audit visibility and traceability. This software automates various audit processes, enabling businesses to focus on growth and risk management rather than spending excessive time on audit findings.
Key features:
- Mobile capabilities for flexible access on different devices and platforms
- Comprehensive coverage of the entire audit process, from planning to monitoring
- Dynamic search functions to meet specific business needs
- Integration with SAP Risk Management and SAP Fraud Management, as well as SAP Process Control and SAP Access Control, enabling a unified audit management function across the organization
➡️
Best suited for: Large enterprises using SAP ERP, particularly those with complex audit requirements in industries such as finance, healthcare, and manufacturing.
Pros:
- Effective project management capabilities, including resource planning and tracking, which help meet specific requirements
- Streamlines internal auditing processes, reducing audit time and costs
- User-friendly interface with drag-and-drop functionality and intuitive navigation
- Integration with SAP Risk Management, SAP Process Control, and Access Control
- Flexible deployment options, both on-premise and cloud-based
Cons:
- Data functionality could be made more practical
- Navigation may be complicated for new users, requiring simplification for a better user experience
- Limited to auditing SAP systems; separate audit management tool needed for organizations using other ERP systems
- Expensive for small organizations
- Integrated solution; continuous solution preferred
- Limited predictive audit functionality
- Big data functionality may be more marketing-driven than a practical reality
Pricing: Custom pricing is available upon request
2. AuditBoard
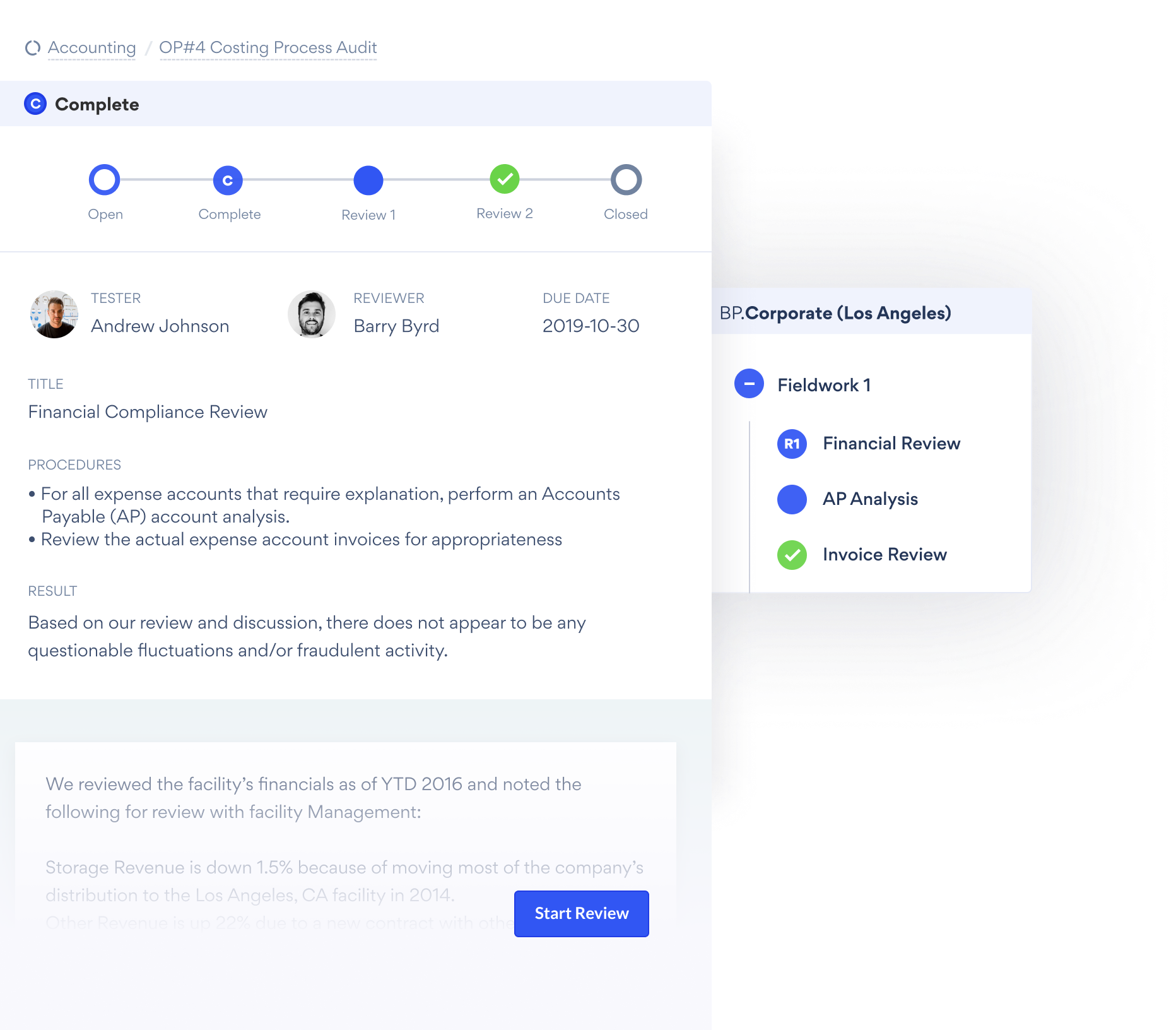
AuditBoard’s connected risk platform is designed to elevate audit, risk, ESG, and compliance programs by consolidating critical organizational data in a unified data core, including risks, controls, policies, frameworks, and issues. The platform offers a suite of applications, namely RiskOversight, CrossComply, OpsAudit, SOXHUB, TPRM, and ESG, which leverage this foundation to streamline audit processes, enhance internal controls, and facilitate operational excellence.
Key features:
- Audit scoping, risk assessment, and project management
- Workpaper and evidence management with support for various file formats, enabling easy access and collaboration
- Issue tracking, reporting, and customizable dashboards
- Integration with other GRC tools and Microsoft Office
- Customizable views, permissions, and workflows
- Internal audit performance management
- Time and expense management
➡️
Best suited for: Mid-sized to large organizations across various industries seeking a comprehensive GRC solution to manage audit, risk, compliance, and ESG programs.
Pros:
- User-friendly interface with intuitive features like drag-and-drop functionality and pinnable tabs
- Centralized repository for audit documentation, enabling easy access and collaboration among team members
- Extensive customization options for views, reports, and workflows
- Responsive customer support and comprehensive training resources
- Continuous product enhancements based on user feedback and evolving industry needs
- Ability to maintain a detailed audit trail
Cons:
- Certain modules can be confusing or seemingly redundant
- Reporting features can be clunky at times, and Excel links do not update automatically
- Offline functionality is limited, with synchronization issues after extended periods without an internet connection, which may be a drawback for teams conducting offsite fieldwork
Pricing: Custom pricing available upon request
3. Workiva
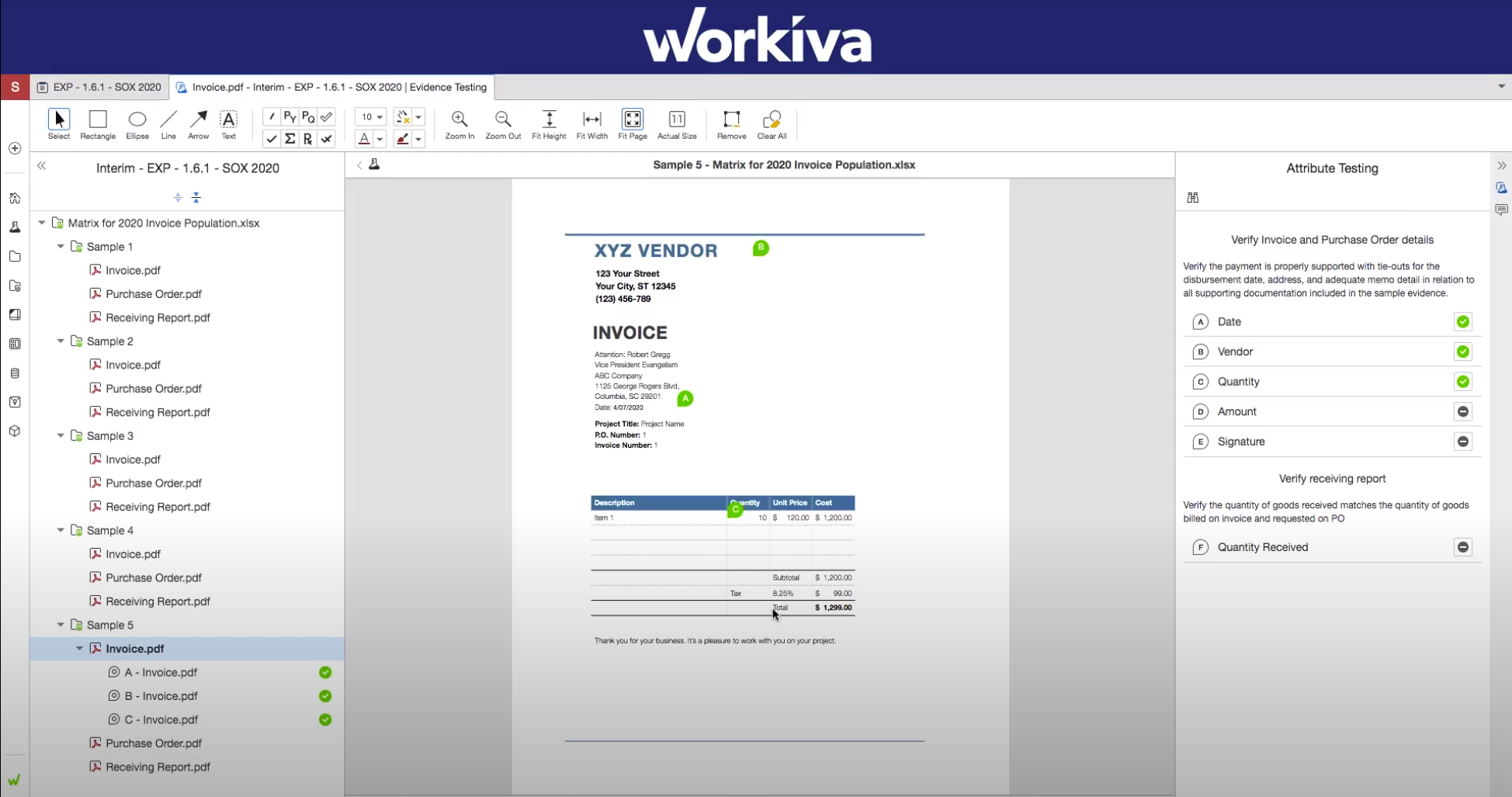
Workiva is a comprehensive platform that effortlessly combines data, teams, and processes related to financial reporting, ESG goals, audits, and risk management. Addressing the growing complexities arising from new regulations, stakeholders, and data sources, Workiva streamlines tasks and ensures trust and transparency in all outputs, including annual reports, SEC filings, climate disclosures, board decks, and audit committee presentations.
Key features:
- Centralized data management and linking capabilities for consistency across reports
- Real-time collaboration and document review options for efficient teamwork
- Customizable dashboards and ad-hoc reporting for data visualization and analysis
- Integration with Microsoft Office and other systems for seamless data flow
- Certifications and attestations for enhanced control and audit trails
➡️
Best suited for: Mid-market to enterprise-level organizations across various industries, particularly those responsible for financial reporting, SEC filings, audit management, and compliance.
Pros:
- User-friendly interface with features similar to Microsoft Office, making it easy for users to adapt
- Powerful linking capabilities that ensure data consistency and reduce manual effort
- Excellent collaboration tools that enable real-time teamwork and review processes
- Extensive customization options for reports, dashboards, and workflows
- Responsive customer support and comprehensive training resources
Cons:
- Occasional slowdowns or performance issues, especially when working with large datasets or multiple users
- Limited offline functionality, with most features requiring an internet connection
- Certain advanced features, such as XBRL tagging, may have a steeper learning curve
- Higher price point compared to some alternatives, though many users find the value justifies the cost
- Limited reporting formats, leaving room for improvement in this area
Pricing: Custom pricing available upon request
4. TeamMate+
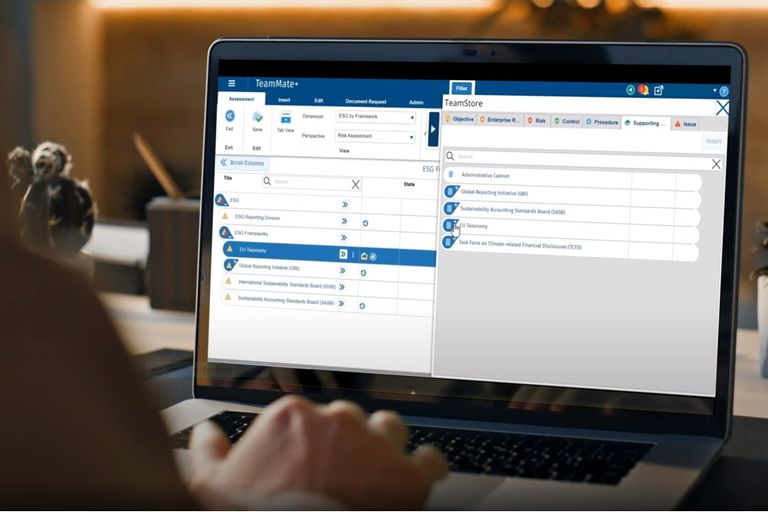
TeamMate+ is an end-to-end audit management system designed to optimize workflows for efficiency and effectiveness. From establishing annual plans to audit planning, fieldwork, reporting, and follow-up, TeamMate+ streamlines the entire audit process. The platform offers decisive integration to enable collaboration with stakeholders and real-time data collection, providing valuable insights to all involved.
Key features:
- Compliance management, issue management, and workflow management
- Risk assessment and audit planning
- Mobile access and alerts/notifications
- Dashboard, forms management, and asset tracking
- Task management and time tracking
- Integration with MS Office products and PDF, enhancing functionality
➡️
Best suited for: Organizations of all sizes, looking for a comprehensive, user-friendly solution to manage end-to-end audit process, with flexible configuration options in alignment with work methodologies.
Pros:
- User-friendly layout with improved navigation, making it easy for users to adapt and use the platform effectively
- Flexible configuration options in alignment with work methodologies, allowing audit departments to tailor the suite to their specific needs
- Comprehensive coverage of the entire audit process, with all modules accessible from a single window, improving efficiency and ease of use
- Integration with MS Office products and PDF, enhancing functionality and streamlining workflows
- Customizable features that allow audit departments to tailor the suite to their unique requirements
Cons:
- The project dashboard with multiple tabs for project search may be cumbersome
- Limited capability to customize reporting templates according to organizational needs, requiring additional effort to fit customizations
- Lack of integration with payroll systems for timesheet management, which may lead to manual processes
- Some functionality used by teams in TeamMate AM is missing in TeamMate+, potentially causing a learning curve for users transitioning from the previous version
- Report editing is often required to fit customizations, adding to the workload
- No offline sync capability and absence of a “Contributor” role in issue management, which may limit flexibility in certain scenarios
Pricing: Custom pricing available upon request
5. Hyperproof
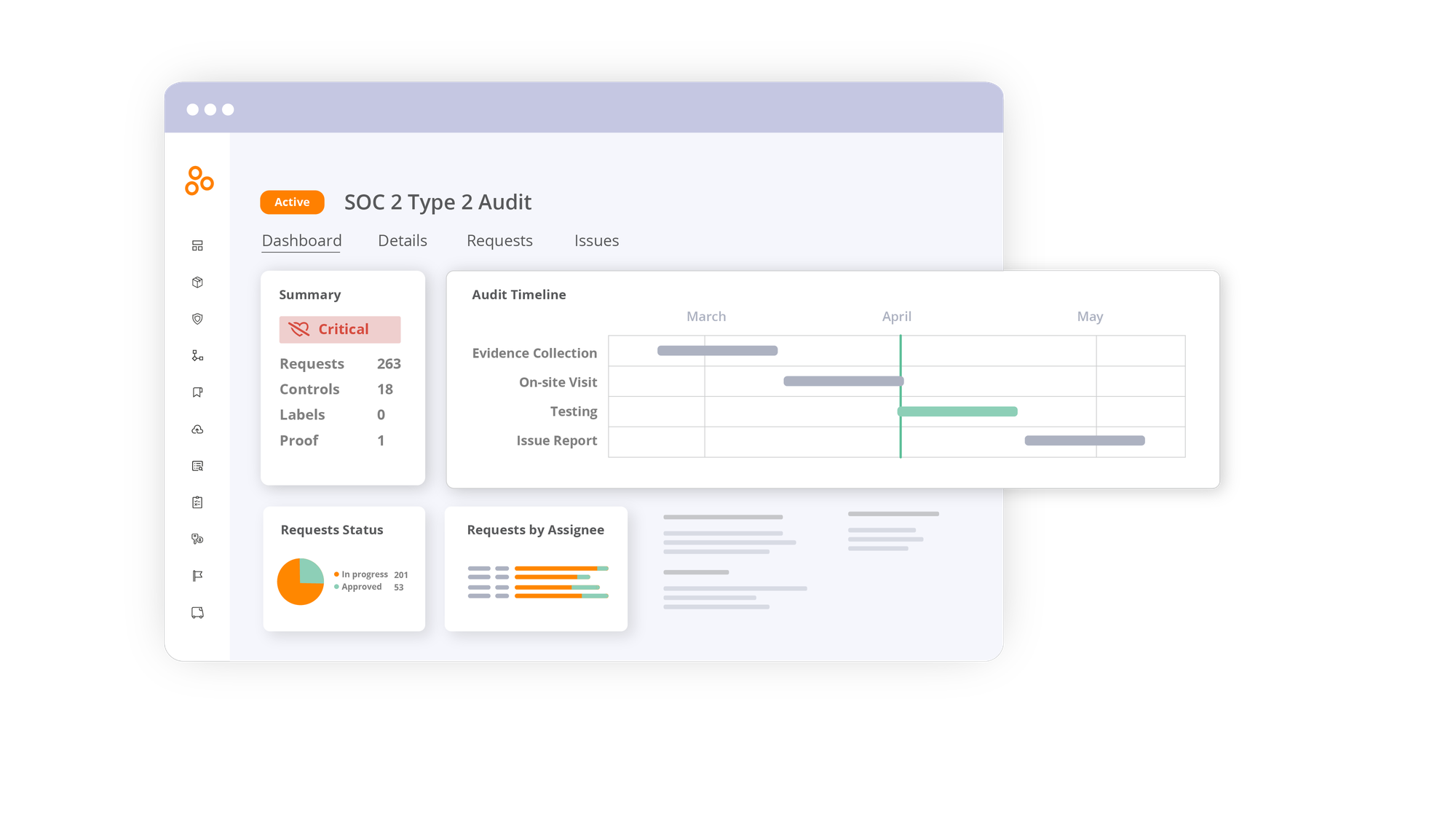
Hyperproof is a security compliance management software that empowers compliance, risk, and security teams to stay on top of all compliance work and continuously manage organizational risks. The platform helps compliance professionals effectively manage and automate their ever-growing compliance workloads, add new frameworks as their companies scale, and easily collaborate across teams.
Key features:
- Compliance management and risk assessment
- Automated evidence collection and mapping to controls
- Customizable workflows and collaboration tools
- Intuitive dashboard for tracking compliance status
- Integration with third-party tools like Google Drive and Asana
➡️
Best suited for: Mid-market to enterprise-level organizations across various industries, particularly those in highly regulated sectors.
Pros:
- User-friendly interface with intuitive navigation, making it easy for users to adapt and perform tasks
- Automated evidence collection and mapping to controls, saving time and reducing manual efforts
- Customizable workflows and flexibility to adapt to organization-specific needs
- Continuous product improvements based on user feedback and evolving compliance requirements
Cons:
- Occasional bugs or slow loading times, which can hinder productivity
- Limited customization options for reports and dashboards, requiring manual workarounds or additional feature requests
- Learning curve for new users, particularly when setting up complex workflows or understanding access permissions
- Integration with certain third-party tools, such as cloud provider Hypersyncs, may require significant effort to operationalize
Pricing: Custom pricing available upon request, with Professional, Business, and Enterprise plans
6. Diligent One

Diligent One Platform, previously known as HighBond, is an enterprise governance software platform designed to fortify security, audit, compliance, assurance, and risk management practices. By centralizing workflows and providing real-time data aggregation, Diligent empowers teams to make informed decisions and streamline reporting. This comprehensive platform caters to all aspects of governance, risk, and compliance (GRC) programs, offering a unified solution for managing various critical functions.
Key features:
- Integrated analytics capabilities for data-driven decision-making
- Customizable platform with flexible configurations to meet specific organizational needs
- One-click reporting for efficient communication and collaboration
- API support for seamless integration with existing systems
- Comprehensive help documentation and a supportive global user community
➡️
Best suited for: Mid-sized to large enterprises across various industries seeking a comprehensive GRC solution to manage audit, risk, compliance, and ESG programs.
Pros:
- Intuitive user interface with easy navigation once the optimal workflow is defined
- Customizable configuration options to meet clients’ specific goals
- Robust analytics and reporting functionalities for enhanced visibility and insights
- Consistent delivery of desired outcomes, assisted by the implementation of Robots to handle intricate situations and propose effective workarounds
Cons:
- Implementation may require assistance from Diligent consultants
- Licensing structure can be complex and may require clarification
- Excessive clicks are required within Projects to navigate to the desired page
- Complexity in understanding user profiles for Contributor and Oversight roles
- The inefficient user experience when applying filters in Results due to double-click requirement
- Limited reporting capabilities without advanced ACL for Windows skills, as computed fields are unavailable in Results
Pricing: Custom pricing available upon request
7. DataSnipper
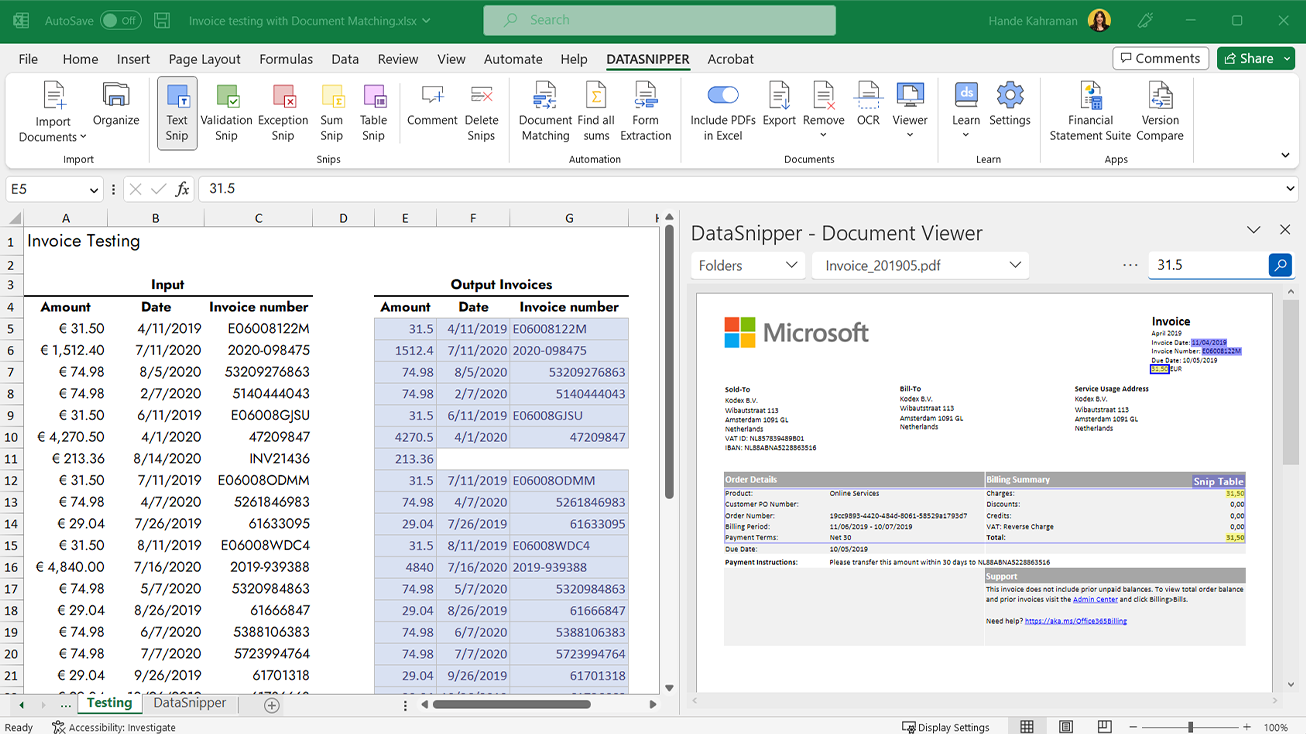
DataSnipper is an intelligent automation platform within Excel that accelerates audit and finance teams’ productivity. The software helps eliminate repetitive tasks, extract, cross-reference, and document the source of any audit and finance procedure. It offers ease of use, time-saving capabilities, and the ability to bridge the gap between PDF and Excel
Key features:
- Automatic text recognition and extraction from scans, images, and PDFs in multiple languages
- Table and data extraction from documents with consistent layouts
- Document matching and comparison
- Integration with Microsoft Excel for seamless data transfer and analysis
- Customizable templates and workflows for efficient audit processes
➡️
Best suited for: Small to mid-sized businesses that process financial documents, such as invoices, receipts, and bank statements, using Excel.
Pros:
- User-friendly interface and easy integration with Microsoft Excel, making it accessible to users with varying technical expertise
- Significant time savings by automating repetitive tasks, such as data entry and document review
- Accurate text and table extraction from various document formats, reducing manual errors
- Multilingual support for automatic text recognition, catering to a global user base
- Customizable templates and workflows to adapt to organization-specific audit processes
Cons:
- Occasional issues with text recognition accuracy, particularly for documents with complex layouts or poor-quality scans
- Longer loading times when working with large volumes of documents or data
- Limited functionality for extracting data from non-standard document formats or inconsistent layouts
- Missing advanced features, such as setting options for opening document previews in separate windows
Pricing: Custom pricing available upon request, with Basic, Professional, and Enterprise plans
8. AppZen
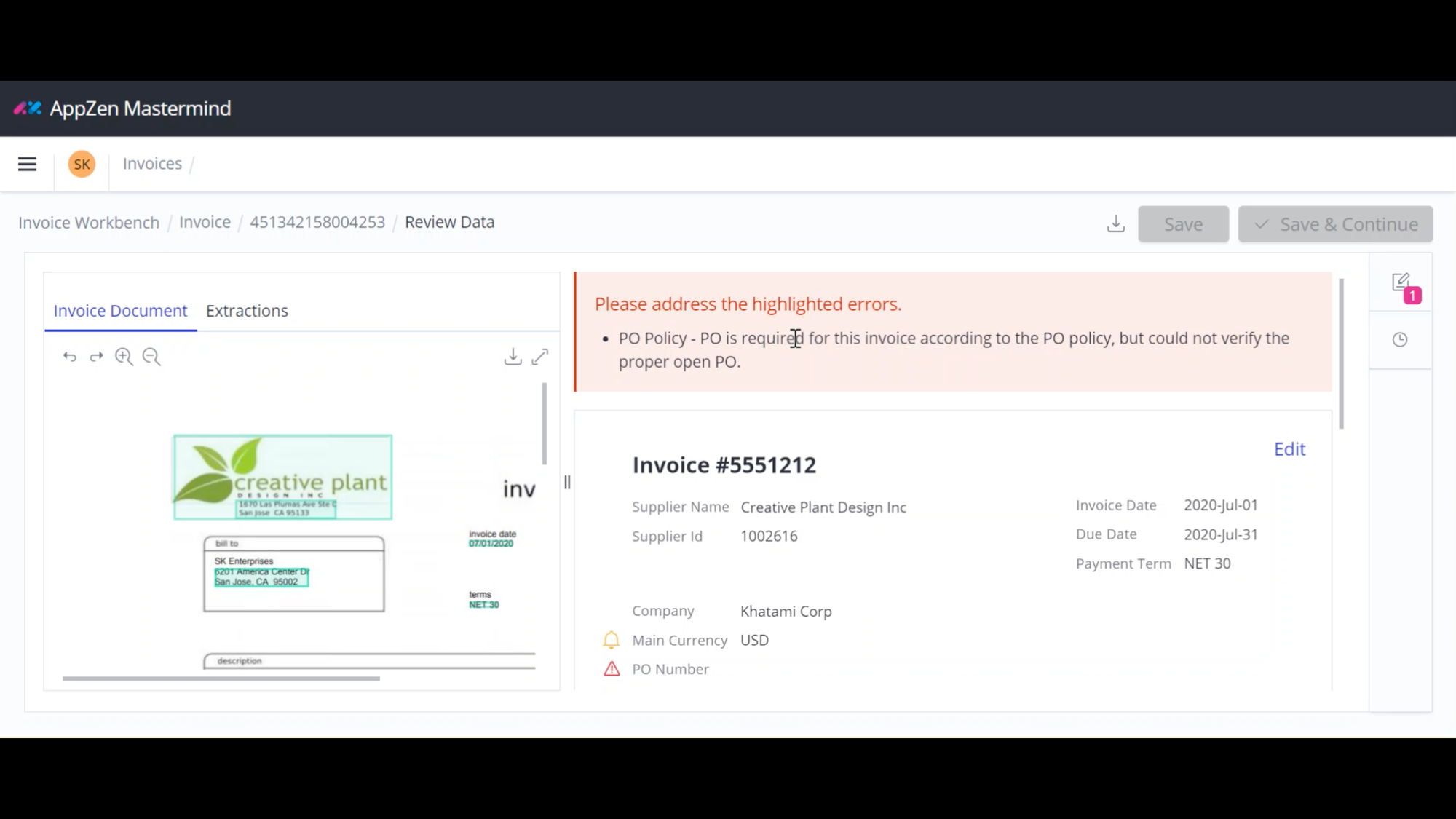
AppZen is a finance AI solution that simplifies travel, expense, card, and accounts payable processing tasks by automating complex workflows, policy checks, and approvals. The AI learns your unique spend profile to independently read and take action on more and more documents over time, fitting into current systems with minimal change management.
Key features:
- Prepayment audit and compliance checks on line items
- Better risk detection
- Support for 40+ languages, eliminating the need for translation services
- Faster employee reimbursements
- Adaptable, customizable solutions for a wide range of business challenges
Best suited for:
- Global enterprises looking to automate complex finance processes and reduce costs
- Organizations with high volumes of travel & expense, card, and accounts payable transactions
- Companies seeking to improve compliance and risk detection across multiple languages and locations
Pros:
- Significant time savings in auditing expense reports
- Accurate detection of duplicates, fraud, and policy violations
- Customizable audit rules and models to fit company-specific needs
- Responsive customer support and continuous product improvements based on user feedback
- Integration with popular expense management systems like Concur
Cons:
- Complex initial setup and configuration, requiring dedicated time and effort
- Limited customization options for more advanced or company-specific audit rules
- Occasional inaccuracies in detecting handwritten or non-standard receipts
- Higher pricing compared to some alternatives, which may be a consideration for smaller organizations
- Some limitations in reporting capabilities and integration with certain ERP systems
Pricing: Custom pricing available upon request
9. Ideagen Internal Audit
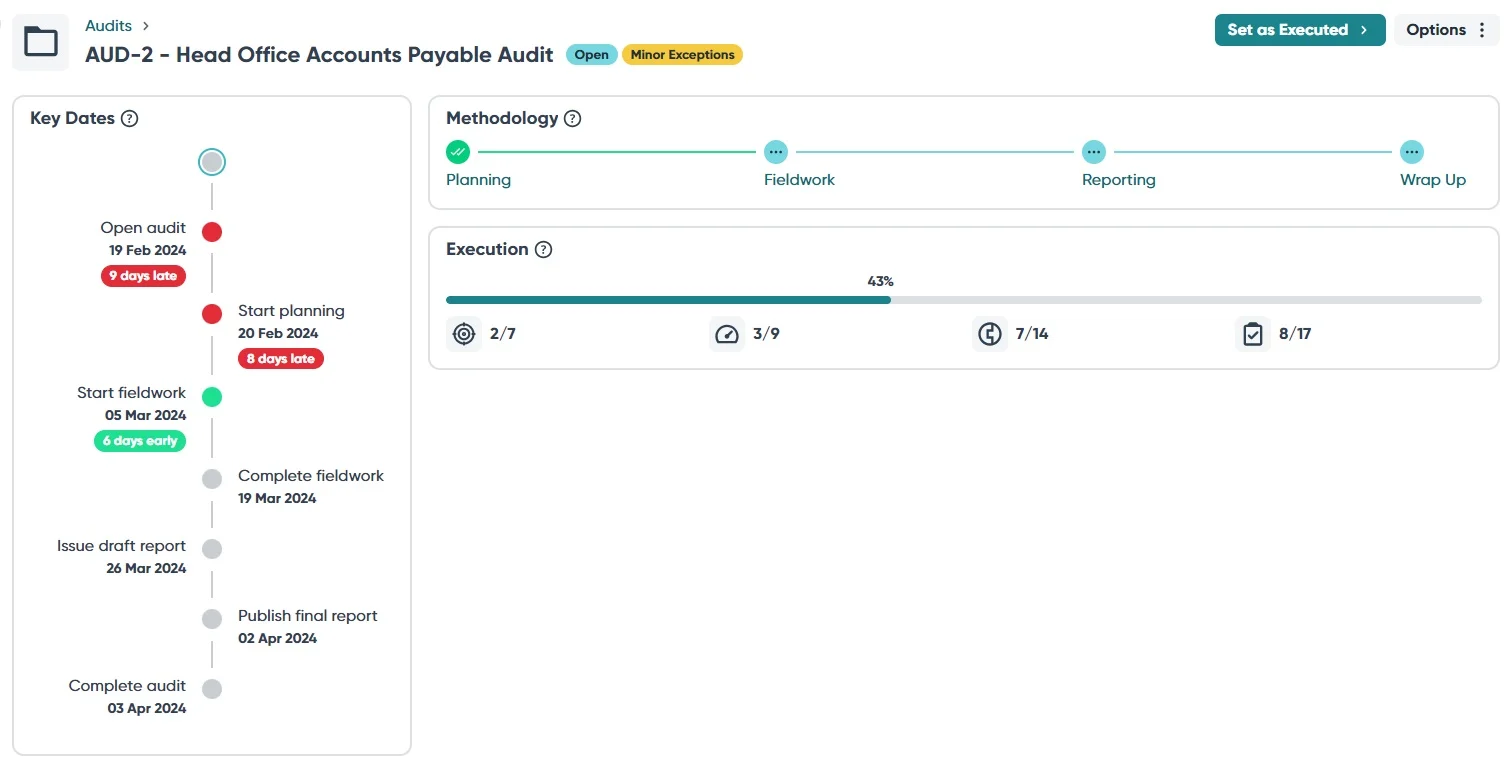
Ideagen Internal Audit (formerly known as Pentana Audit) is comprehensive audit management software designed to connect various aspects of the audit process and manage the entire audit lifecycle. Leveraging risk and control frameworks, the program facilitates internal audits and offers functionalities such as compliance management, exception management, issue management, risk assessment, and internal controls management.
Features:
- Compliance with various standards and regulations, including SOX, ISO, ESG, and COSO
- Live data dashboards and reporting
- Remediation activities to mitigate identified risks
- The central library of objectives, risks, controls, and tests (ORCT) for consistent audit activities
- Collaborate easily with auditees through clear processes, sampling, and questionnaires
- Seamless integration with Ideagen Risk Management for a comprehensive view of risks and audit issues
- Data integration from across the business for enhanced visibility and analysis
➡️
Best suited for: Organizations of various sizes seeking a comprehensive solution to manage their end-to-end audit process, with customization options to align with their specific needs.
Pros:
- Easy setup and helpful support team during the installation
- Provides an organized approach to managing audit findings and workstreams
- Intuitive system for risk assessment, control management, and report creation
- Cost-effective compared to similar products, with smooth implementation and good customer service
- Intuitively designed audit scopes, plans, and work papers, with the simple attachment of supporting documents
Cons:
- Some end-user aspects could use improvement, and accessing assistance may not be straightforward
- Creating companies within others can be challenging for growing companies
- Limited customization options and bureaucracy in the system, requiring multiple clicks to progress
- Report generation may require adjustments and programming knowledge for advanced customization
- Initial setup and configuration may be time-consuming and require effort
- Potential synchronization issues during collaborative work
- Restricted ability to link different audits or documents
Pricing: Custom pricing available upon request
10. Xelix
Xelix is a cloud-based auditing software that offers an AI-powered Control Centre for Accounts Payable teams. The platform supports overpayment and fraud prevention, master vendor data management, supplier statement reconciliation, vendor query management, and AP/P2P reporting.
Key features:
- Duplicate invoice and payment detection
- Invoice error identification and prevention
- Supplier statement reconciliation
- Vendor master data management and fraud prevention
- AP/P2P reporting and analytics
➡️
Best suited for: Large enterprises with complex AP processes and high transaction volumes seeking to reduce overpayments, fraud, and manual reconciliation efforts.
Pros:
- User-friendly interface and straightforward setup with minimal technical integration required
- Proactive identification of potential duplicate invoices and payments, preventing cash leakage
- Significant time savings in supplier statement reconciliations and audit preparation
- Continuous product development based on client feedback and requirements
Cons:
- Some company-specific customization may be required for certain features, such as statement reconciliations
- Reporting capabilities may need further enhancement to meet specific organizational needs
- Limited historical data and reporting available during initial implementation
Pricing: Custom pricing available upon request
11. Suralink
Suralink provides accounting and other professional service firms with a single, secure platform to collaborate with clients, exchange documents at scale, and track engagement progress. With enterprise-grade security and an easy-to-use interface, Suralink helps firms increase efficiency and improve client relationships.
Key features:
- Secure document sharing and collaboration with clients
- Customizable request lists and document organization
- Real-time progress tracking and status updates
- Intuitive user interface for both firms and clients
- Communication tools, including comments and notifications
➡️
Best suited for: Accounting firms, including tax, advisory, and audit practices and professional service firms, such as legal services, security consulting, and financial services
Pros:
- User-friendly interface that is easy for both firms and clients to navigate and adopt
- Centralized platform for secure document sharing, eliminating the need for multiple tools and email exchanges
- Customizable request lists and categories for organizing and tracking documents
- Real-time visibility into engagement progress, with status updates and completion percentages
- Responsive customer support and ongoing product enhancements based on user feedback
Cons:
- Occasional website downtime or server issues, which can temporarily disrupt access to the platform
- Some limitations in customization options, such as the inability to move client files between requests or merge multiple engagements
- Certain features, such as the chat window, may appear cluttered or complex
- Clients with limited technical expertise may require additional guidance or support in navigating the platform
Pricing: Custom pricing available upon request
12. Nanonets
Nanonets is an AI-powered intelligent document processing platform that revolutionizes financial audit automation. With cutting-edge OCR capabilities, machine learning algorithms, and robust PII data masking features, Nanonets streamlines the audit process, boosts operational efficiency, and ensures the utmost protection of sensitive financial information.

It automates data extraction with an accuracy rate of over 95%, allowing you to analyze thousands of documents in a fraction of the time it would take manually. Nanonets seamlessly integrates with your ERP systems, making the process a breeze.
Key features:
- Centralized financial audit operations, bringing all audit-related tasks and data into a unified platform
- AI-driven data extraction from financial documents with over 95% accuracy, analyzing thousands of documents in a fraction of the time
- Automated expense recognition and classification, seamlessly integrating with ERP systems
- Powerful workflow capabilities for financial risk assessment, incorporating custom rules and a human-in-the-loop model
- Secure log of all financial activities, maintaining a digital archive of financial documents for easy retrieval during audits
- One-click integrations with popular ERP and payment software, simplifying integration with existing financial workflows
- Robotic process automation (RPA) capabilities for analyzing historical financial data, generating financial statements, and making data-driven forecasts
- Advanced PII data masking features to protect sensitive financial information during the data extraction process
➡️
Best suited for: Medium to large enterprises that deal with large volumes of financial documents, seeking to optimize their financial audit workflows and enhance operational efficiency,
Pros:
- Significantly reduces manual efforts and minimizes the risk of errors and discrepancies in financial audits
- Enhances financial data accuracy, review readiness, and transparency during audits
- Ensures compliance with financial audit requirements through secure data management and digital archiving
- Ensures compliance with data privacy regulations and safeguard your organization’s reputation
Cons:
- Initial setup and configuration may require some time and resources
- Not a full-fledged audit automation software
Pricing: Forever free and pay as you go plans available. Premium plan starts from $999/month.
Implementing audit automation software

Selecting the right audit automation software is crucial for streamlining your organization’s auditing processes. When evaluating different options, consider the following key factors:
- Functionality: Ensure the software aligns with your specific auditing requirements and offers risk assessment, workflow management, and reporting features.
- Ease of use: Look for an intuitive user interface that allows your team to adopt and utilize the software effectively and quickly.
- Integration: Assess the software’s ability to integrate with your existing systems, such as ERP, accounting, or GRC platforms, for seamless data flow and visibility.
- Scalability: Choose a solution that can grow with your organization’s evolving needs, handling increasing data volumes and complexity.
- Security and compliance: Verify that the software meets your organization’s data privacy and security standards and any industry-specific regulatory requirements.
To ensure a successful implementation, follow these best practices:
- Define clear goals and objectives for your audit automation initiative, aligning them with your organization’s overall strategy.
- Involve key stakeholders from audit, finance, IT, and other relevant departments to foster collaboration and buy-in.
- Conduct thorough testing and pilot projects to identify and address potential issues before full-scale deployment.
- Provide comprehensive training to your audit team, ensuring they understand how to use the software and leverage its capabilities effectively.
- Establish a governance framework for access, permissions, and workflows within the audit automation software.
- Continuously monitor and measure the performance of your audit automation solution, making data-driven decisions for ongoing optimization.
Types of audit automation technologies and use cases

Audit automation is not a one-size-fits-all solution. It encompasses diverse technologies, each with unique capabilities and applications in the auditing process. Understanding these technologies and their use cases is crucial for organizations looking to optimize their audit workflows and derive maximum value from their automation investments.
Data integration and analytics
The foundation of effective audit automation lies in the ability to integrate and analyze vast amounts of financial data from multiple sources. Advanced data integration tools extract, transform, and load (ETL) data from various systems, such as ERP, CRM, and accounting software, into a centralized repository. This centralized data enables auditors to gain a comprehensive view of an organization’s financial health and identify potential risks or anomalies.
Powerful data analytics tools then come into play, performing calculations, identifying patterns, and highlighting outliers or exceptions that may indicate potential issues. For example, an auditor can use data analytics to compare financial performance against budgets and forecasts, identify unusual transactions or journal entries, analyze trends and fluctuations in key financial metrics, and detect potential fraud or non-compliance with internal controls.
Predictive analytics and machine learning
Predictive analytics and machine learning take audit automation to the next level, enabling auditors to anticipate potential risks and issues before they occur. These technologies analyze historical data and identify patterns, allowing auditors to assess the likelihood of financial statement errors or misstatements, predict the risk of fraud or non-compliance in specific business areas, identify potential weaknesses in internal controls, and prioritize audit focus areas based on risk levels.
Machine learning algorithms continuously improve their accuracy and effectiveness over time as they learn from new data and feedback, making the audit process more efficient and targeted.
Robotic Process Automation (RPA)
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) is another powerful tool in the audit automation arsenal. RPA uses software “bots” to automate repetitive, rule-based tasks, such as data entry and validation, reconciliations and comparisons, report generation and distribution, and follow-up on audit findings and recommendations.
RPA frees up auditors to focus on more strategic, value-added activities while reducing the risk of human error and ensuring consistency in the execution of audit procedures.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Cognitive Technologies
AI and cognitive technologies, such as optical character recognition (OCR) and NLP, are increasingly used in audit automation to analyze unstructured data, such as contracts, emails, and images.
These technologies help auditors extract key terms and clauses from contracts and agreements, identify potential risks or non-compliance issues in email communications, verify the accuracy and completeness of financial statements and disclosures, and detect anomalies or inconsistencies in images, such as invoices or receipts.
AI and cognitive technologies enable auditors to better understand an organization’s financial health and risk profile, providing more valuable insights and recommendations.
Use cases in the audit process
Modern audit systems apply the above-mentioned technologies throughout the audit process to enhance efficiency, accuracy, and effectiveness. Some specific use cases include:
- Risk assessment: Predictive analytics and machine learning identify high-risk areas and prioritize audit focus
- Audit execution: RPA and data analytics automate testing procedures and identify exceptions or anomalies
- Reporting: AI and cognitive technologies generate insights and recommendations based on audit findings
- Continuous monitoring: Real-time monitoring solutions detect potential issues and risks on an ongoing basis
Organizations embracing these audit automation technologies and applying them strategically throughout the audit process can transform their internal audit function into a proactive, value-driven partner supporting business objectives and driving continuous improvement.
Final thoughts
As the demands on audit teams grow in complexity and volume, embracing audit automation becomes increasingly crucial. Investing in the right software and implementing it effectively can help you transform your audit function into a proactive, value-driven partner that supports business objectives and drives continuous improvement.
Don’t let manual processes and inefficiencies hold your audit team back any longer. Explore Nanonets today and unlock the full potential of your audit function. Schedule a demo now and experience the benefits firsthand.
FAQs
Can audit be fully automated?
While audit automation has significantly advanced, achieving full automation in audits remains challenging. Certain audit tasks, such as analyzing complex transactions or interpreting qualitative information, require human judgment and expertise. While technology can streamline data collection, analysis, and risk assessment, human auditors are essential for critical thinking and understanding the context of audit findings. However, continuous advancements in artificial intelligence and machine learning may further automate certain audit aspects. While full automation may not be attainable due to the complexity of audits and the need for human judgment, ongoing developments in technology will continue to enhance audit efficiency and effectiveness.
How is automation used in auditing?
Automation is extensively used in auditing to streamline and optimize various processes. Audit software and tools automate data collection from diverse sources, consolidating it for analysis. Automated data analysis identifies patterns, trends, and anomalies, flagging potential risks or errors for further investigation. Risk assessment models are applied using automation, aiding auditors in identifying high-risk areas. Control testing can be automated to validate compliance. Audit workflow automation also enables task management, issue tracking, and reporting. Although full automation of audits remains a challenge due to the need for human judgment and interpretation, automation significantly enhances audit efficiency, accuracy, and effectiveness, empowering auditors to focus on critical aspects of the audit.


