Whether you’re a small business or a large corporation, implementing effective purchase order management can make a significant difference in your operations.
In this blog, we’ll walk through
- what purchase order management is,
- why it is important,
- how to implement it effectively,
- how to automate it using technology.
What is Purchase Order Management?
Purchase order management is the process of managing the creation, approval, tracking, and fulfilment of purchase orders in your business.
It ensures that all procurement activities are carried out systematically and in compliance with the business’ specific policies around procurement.
What are the benefits?
With proper purchase order management in place, a business’ procurement function reaps multiple benefits –
- Better Supplier Relationships: Effective purchase order management ensures that orders are communicated clearly and payments are made on time. This reliability fosters trust and strengthens relationships with your suppliers.
- Data-Driven Planning and Insights: Businesses can leverage detailed data maintained from purchase orders to analyze spending patterns, strategize budgets and identify cost-saving opportunities.
- Cost Savings: Implemented properly, purchase order management systems ensure that businesses can negotiate better terms with suppliers, avoid duplicate orders, reduce administrative costs, and avail early payment discounts.
- Visibility and Control: A centralized system provides real-time tracking of purchase orders, which helps track order status and ensure timely fulfillment, leading to efficient procurement operations.
Elements of Purchase Order Management
An effective purchase order management system essentially comprises of 7 elements as below –
Creation: This is the initial stage that includes order generation from the requisition from the particular department. The purchase order document specifies items to be purchased, quantity, rate, date of delivery and should be within the procurement policy of the company.
Review: Once a purchase order is issued, consideration needs to be given to how the process is reviewed and approved. This step makes sure the order is required, funded and will not contradict the regulations internally or externally. This is where Approval processes and hierarchies are usually defined.
Followup: When the purchase order approved it is sent to the supplier and its progress is to be followed up. This consists of tracking that the suppliers have acknowledged and submitted the supplies at the right time, or to the admin at the proper time.
Fulfillment: When the order arrives, it is checked for quality and quantity. Any discrepancies are immediately addressed and once everything is confirmed to be in order, the purchase order is marked as fulfilled.
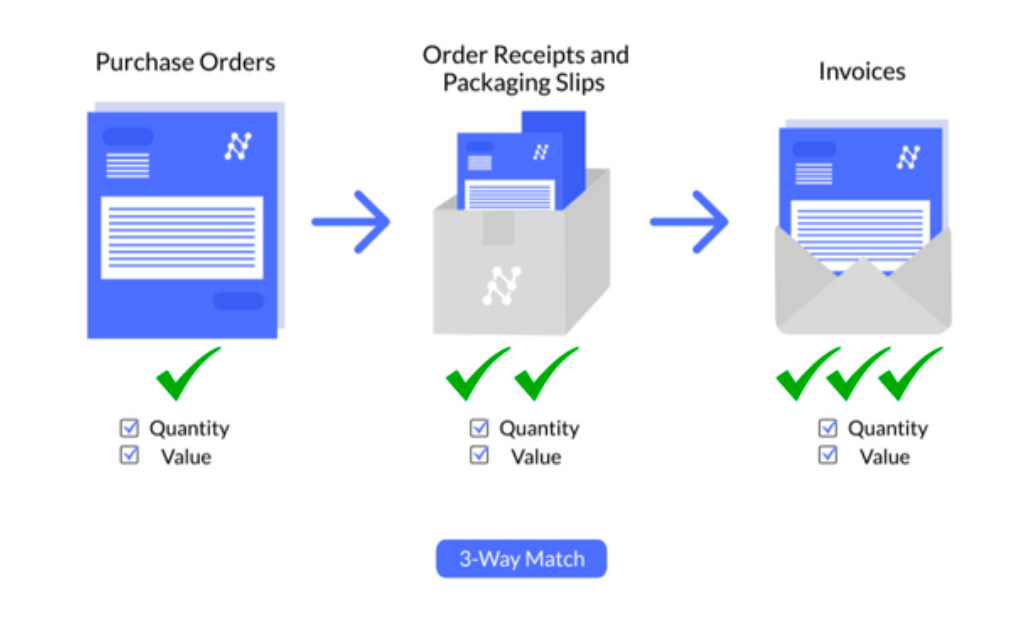
3 Way Matching: The process of verifying that all documents involved in the procurement process match in terms of item details, quantities and prices. 2-way matching checks a purchase order against an invoice while, 3-way matching includes the receiving report as well. Such a process guarantees that the business pays for exactly what was ordered and received to avoid overpayments, frauds or irregularities.
ERP/Accounting Software Sync: Syncing purchase order management with ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) or accounting software ensures that every procurement record is automatically synced up. This is essential for real-time and accurate financial visibility, and aids in strategic budgeting as well.
Record Keeping: Maintaining accurate records of all purchases and documenting every process in the procurement cycle is very important for reconciliation, auditing and fraud detection.
Implementing Purchase Order Management
Let’s walk through a guide on how a business can optimize their procurement and PO management by following the 4 steps below –
Step 1: Create a Procurement Policy
Before getting started, businesses need to have a procurement policy in place.
The procurement policy should define rules and spending limits, along with defining approval processes required for the processing of a purchase order.
We have a comprehensive blog covering why a procurement policy is important to have in place, and how to create one tailored for your business’ needs –
Expense Policy 101: How to Create & Implement your Policy
An expense policy dictates how employees can use company funds. Learn to craft an effective expense policy & process to guide employee spending.

Step 2: Choose Software to maintain POs
Businesses also need a system to document each purchase.
While small businesses might see sense in maintaining their purchase records in Excel or other such database, it is still advisable to go for a dedicated procurement software to document a business’ purchases. Why?
- they provide easy purchase requisition forms and templates for POs.
- They help in keeping records of verified suppliers.
- POs can be automatically emailed / sent in other way to suppliers.
Step 3: Review your PO Workflow
Make sure your PO workflow is in line with the basic principles of PO management discussed above.
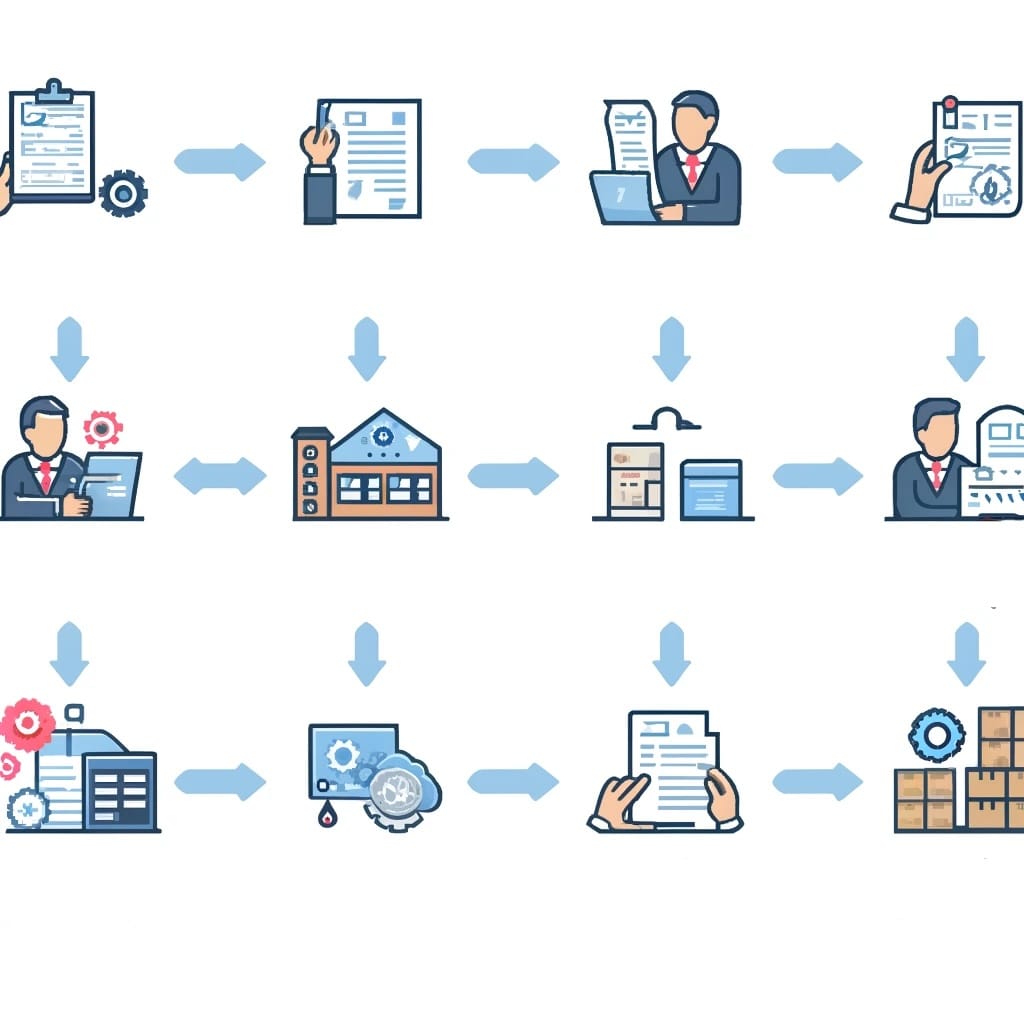
Below is an example of an effective PO workflow.
Need Identification and Requisition
Employees should be trained to identify and document procurement needs accurately.
An employee, say in the marketing department identifies the need for promotional materials for an upcoming campaign.
The employee fills out a requisition form, detailing the items needed, quantities, and desired delivery date.
Requisition Review
We now need to ensure that requisition forms align with the company’s procurement policy. The requisition form is submitted to the procurement department, where it needs to be reviewed for accuracy, necessity, and budget alignment.
Purchase Order Creation
The procurement policy must be clear to guide the creation of POs. Once approved, the requisition form would be used to generate a purchase order. The PO includes item descriptions, quantities, prices, delivery dates, and compliance with procurement policies.
Approval Process
The PO is sent through the established approval hierarchy, which includes department heads and financial controllers. Each approver checks the PO for compliance with policies and budget availability.
Order Placement and Follow-Up
Reliable suppliers must be selected and agreements in place. After final approval, the PO is sent to the supplier. The procurement dept follows up to ensure the supplier acknowledges the order and confirms the delivery schedule.
Receipt and Inspection
Upon delivery, the receiving department inspects the goods to ensure they match the PO specifications in terms of quality and quantity. Discrepancies are reported immediately.
3-Way Matching
The procurement dept performs a 3-way match to ensure that the PO, invoice, and receiving report align perfectly. This step confirms that the business pays only for what was ordered and received.
Invoice Processing and Payment
After verification, the supplier’s invoice is processed. The invoice is approved for payment and sent to the finance department which makes the payment.
Record Keeping and ERP/Accounting Software Sync
All documents related to the PO – including the requisition, approvals, supplier communications, delivery receipts, and payment records – are archived for future reference. These records are also synced with the company’s ERP or accounting software.
Step 4: Look for Automation Opportunities
With the foundational elements in place, the next step is to explore automation opportunities to streamline the PO management process further.
Today, procurement automation software can automate the majority of tasks in the p2p cycle.
Here are some key areas to consider:
- Automate Requisition Approval: Use workflow automation to automatically route requisitions through the approval process based on predefined criteria.
- Automate PO Creation: Implement automation that converts approved requisitions directly into purchase orders, reducing manual data entry.
- Supplier Communication: Automate the sending of purchase orders to suppliers via email or EDI (Electronic Data Interchange) systems.
- Tracking and Follow-Up: Use automated tracking systems to monitor order status and send automatic reminders to suppliers and internal stakeholders.
- Receipt and Inspection: Implement barcode scanning and automated receipt systems to streamline the inspection process and update records in real-time.
- Invoice Processing: Automate the capture and validation of supplier invoices using OCR (Optical Character Recognition) technology, and integrate with the finance system for seamless payment processing.
- 3-Way Matching: Use software to automatically perform 3-way matching of POs, invoices, and receiving reports, flagging any discrepancies for review.
- Record Keeping: Use automation to sync purchase data with your ERPs / accounting software.
Today, PO management and automation software can be employed at cheap SaaS subscription costs, and are economically viable.
Here’s an overview of the best ones available in 2024.
6 Best Procure-to-Pay Software in 2024
We explore how procure-to-pay software streamlines processes, highlight key features, and review the 6 best procure-to-pay software today.
Automate PO Management with Nanonets
When we look at any PO workflow, it’s clear that the tasks are manual, prone to errors, and slow. All this is a bottleneck towards achieving effective PO management. Implementing an automation solution can address these challenges effectively.
Here’s how a procurement automation software like Nanonets can transform the workflow –
Purchase Request:
An employee submits a purchase request electronically using the Nanonets portal.
Purchase Order Creation:
Nanonets automatically generates a PO based on the request details, streamlining the process.
Purchase Order Approval:
The PO goes through an automated approval workflow within Nanonets. You can set predefined rules and conditional checks to ensure consistency, reduce errors, and prevent unauthorized spending.

Approval notifications are sent and can be easily managed within popular communication tools like Slack and Microsoft Teams. These notifications include direct Calls to Action (CTAs), making the process straightforward and facilitating quick decision-making.

Purchase Order Dispatch:
Once approved, the system automatically sends the PO to the supplier via integrated email or a supplier portal like SAP Ariba or Coupa.
.png)
Goods or Services Delivery:
The supplier processes the order and updates the delivery status in their portal, which syncs with Nanonets.
Invoice Data Capture and Matching:
Nanonets automatically extracts data from invoices, purchase orders, and delivery notes, reducing manual entry and errors.
Automated three-way matching ensures accuracy by matching invoices, purchase orders, and delivery notes before processing payments.
Payment Processing:
Nanonets facilitates seamless payment processes, ensuring all transactions are completed efficiently and on time.

This helps maintain good relationships with suppliers and avoid late payment penalties.
Integration with ERP/Accounting Software:
Nanonets integrates with various ERP and accounting systems, providing a unified procurement and financial data management experience.

By automating the purchase order workflow with Nanonets, businesses can ensure seamless data flow across various applications, reduce manual errors, and enhance overall efficiency of their p2p cycle – all leading to effective purchase order management.
Is PO Management important for Small Businesses?
Larger companies need well maintained PO systems to manage their procurement processes due to the volume of transactions and employees involved.
Small businesses often operate with limited resources and may question the necessity of implementing a Purchase Order (PO) system. However, there are several compelling reasons why even small businesses can benefit significantly from a PO system:
- Improved Financial Control: Tracks spending and stays within budget by documenting every purchase.
- Streamlined Purchasing: Structures the purchasing process, reducing errors like duplicate orders.
- Enhanced Vendor Relationships: Clear documentation of orders improves supplier relationships and reduces disputes.
- Better Inventory Management: Helps maintain stock levels, preventing overstocking or stockouts.
- Compliance and Audit Trail: Provides a documentation trail for easier compliance with legal and financial regulations.
- Cost Savings: Reduces over-ordering, negotiates better terms with suppliers, and cuts administrative costs.
- Scalability and Growth: Scales with the business as it grows, handling increased order volumes and complex supply chains.
Many PO management systems, like Nanonets, are available as SaaS with flexible pricing, allowing small businesses to access them without large upfront investments.
Implementing a PO management system is a valuable investment, offering improved financial control, efficiency, and scalability, and setting a solid foundation for future growth.



