Petty Cash Reconciliation: What is It, Best Practices, and Automation
Petty cash, also referred to as a small cash fund, is a fixed amount of money reserved for minor expenses in a business. These expenses typically include small purchases like office supplies, travel expenses, or miscellaneous items that are too insignificant to warrant writing a check or initiating an electronic payment.
Despite its small denomination, petty cash plays a significant role in day-to-day operations, offering flexibility and convenience in handling minor expenses without the need for formal approval processes. Petty cash reconciliation is the process of verifying and documenting petty cash transactions to ensure that the amount of cash on hand matches the recorded balance in the petty cash account. It serves as a control mechanism to maintain accurate financial records and prevent misuse or misappropriation of funds.
In this article, we’ll dive into petty cash reconciliation — how best to go about it, common challenges, and how advanced automation solutions like Nanonets can help.
Looking out for a Reconciliation Software?
Check out Nanonets Reconciliation where you can easily integrate Nanonets with your existing tools to instantly match your books and identify discrepancies.
What is Petty Cash Reconciliation?
Petty cash reconciliation refers to the systematic process of comparing the actual cash on hand with the recorded balance in the petty cash account. It involves reviewing and validating petty cash transactions to ensure accuracy and completeness in financial records.
The primary objective of petty cash reconciliation is to identify any discrepancies between the physical cash count and the recorded balance, thereby maintaining the integrity of company financials and ensuring compliance with internal controls and accounting standards.
Businesses typically establish petty cash funds to facilitate the timely payment of small expenses that do not warrant formal procurement processes. However, without proper oversight and reconciliation procedures, petty cash can be susceptible to misuse, errors, or theft. Petty cash reconciliation serves as a safeguard against such risks by providing a structured framework for monitoring and controlling cash disbursements.
What are the Steps Involved in Petty Cash Reconciliation?
During the petty cash reconciliation process, the following steps are typically performed:
- Recording Transactions: All petty cash transactions, including withdrawals and expenditures, are documented with supporting receipts or vouchers.
- Physical Count of Cash: The actual amount of cash remaining in the petty cash fund is counted and verified against the recorded balance.
- Comparison and Analysis: The recorded transactions are compared with the physical cash count to identify any discrepancies or irregularities.
- Adjustments and Corrections: Any discrepancies found during the reconciliation process are investigated, and adjustments are made to reconcile the petty cash account balance.
- Documentation and Reporting: The reconciliation results are documented in a reconciliation report, detailing the findings, adjustments made, and any corrective actions taken. This report serves as a formal record of the reconciliation process and provides transparency and accountability.
Overall, petty cash reconciliation plays a vital role in maintaining financial accuracy, transparency, and control within an organisation. It helps ensure that petty cash funds are used appropriately, expenses are properly accounted for, and financial records are kept up to date and accurate.
Challenges of Petty Cash Reconciliation
Petty cash reconciliation, while essential and seemingly easy, can actually pose several challenges for businesses. Some common ones include:
- Lack of Documentation: Inadequate documentation of petty cash transactions, such as missing receipts or incomplete records, can hinder the reconciliation process and make it challenging to verify expenditures accurately.
- Manual Processes: Relying on manual processes for petty cash reconciliation can be time-consuming and prone to errors. Manual data entry and calculation increase the risk of inaccuracies and discrepancies in financial records.
- Cash Discrepancies: Discrepancies between the recorded balance and the actual cash count may occur due to theft, mismanagement, or human error. Identifying and resolving these discrepancies requires thorough investigation and reconciliation efforts.
- Compliance Risks: Failure to adhere to internal controls and compliance requirements can result in regulatory violations and financial losses. Businesses must ensure that petty cash reconciliation procedures align with established policies and regulatory standards.
- Lack of Accountability: Without clear accountability and oversight, petty cash funds may be vulnerable to misuse or unauthorised expenditures. Implementing robust controls and monitoring mechanisms is essential to mitigate the risk of fraud or misappropriation.
Despite these challenges, businesses can overcome them by implementing effective petty cash management practices and leveraging technology solutions to streamline the reconciliation process.
Best Practices for Petty Cash Reconciliation
To overcome the challenges associated with petty cash reconciliation, businesses can adopt the following best practices:
- Establish Clear Policies and Procedures: Develop comprehensive policies and procedures governing the use of petty cash, including guidelines for recording transactions, approving expenditures, and conducting reconciliations.
- Maintain Adequate Documentation: Require employees to provide detailed receipts or vouchers for all petty cash transactions. Keep accurate records of expenditures, withdrawals, and replenishments to facilitate the reconciliation process.
- Regular Reconciliation: Conduct regular reconciliations of petty cash funds to ensure that the recorded balance aligns with the actual cash count. Schedule reconciliation activities on a weekly or monthly basis to promptly identify and address any discrepancies.
- Segregation of Duties: Implement segregation of duties to prevent fraud and errors. Assign distinct roles and responsibilities for managing petty cash, recording transactions, and conducting reconciliations to ensure accountability and oversight.
- Leverage Technology Solutions: Invest in accounting software or petty cash management systems that automate and streamline the reconciliation process. These tools can help reduce manual effort, improve accuracy, and enhance visibility into petty cash transactions.
By implementing these best practices, businesses can enhance the efficiency, accuracy, and control of their petty cash reconciliation processes, ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements and maintaining financial integrity.
Automating Petty Cash Reconciliation
With advancements in technology, businesses can leverage automation to streamline petty cash reconciliation processes. Advanced Optical Character Recognition (OCR) solutions like Nanonets can automate petty cash reconciliation to save your business time, money, and improve the efficiency and accuracy of petty cash reconciliation:
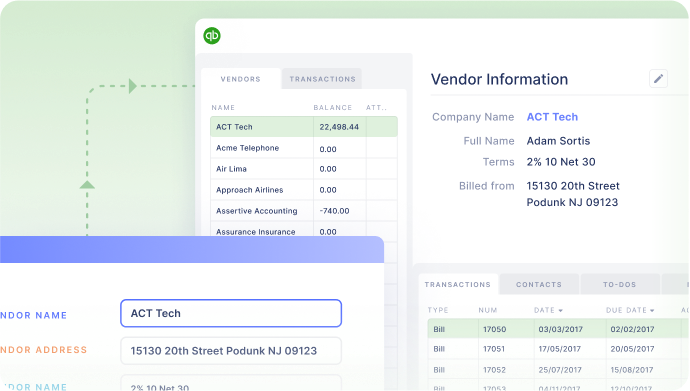
- Digital Receipt Management: Implement digital receipt management solutions that allow employees to upload receipts directly into the system using mobile devices. This eliminates the need for manual receipt collection and ensures that all transactions are documented electronically
- OCR Technology: Advanced Optical Character Recognition (OCR) technologies like Nanonets can extract data from receipts and automatically populate transaction details in the reconciliation system. OCR can accurately capture information such as date, vendor name, and amount, reducing manual data entry errors.
- Integration with Accounting Software: Integrate petty cash reconciliation software with accounting systems such as QuickBooks or Xero to synchronise transaction data in real-time. This ensures seamless communication between financial systems and eliminates the need for manual data transfer.
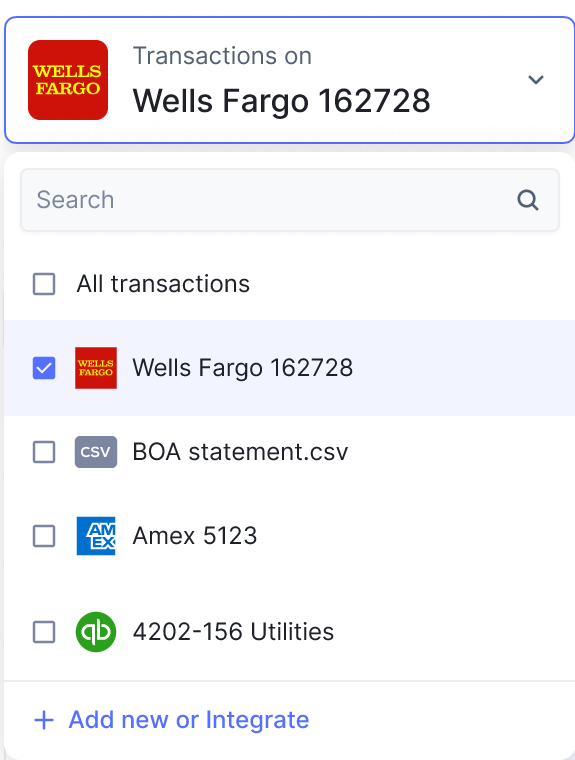
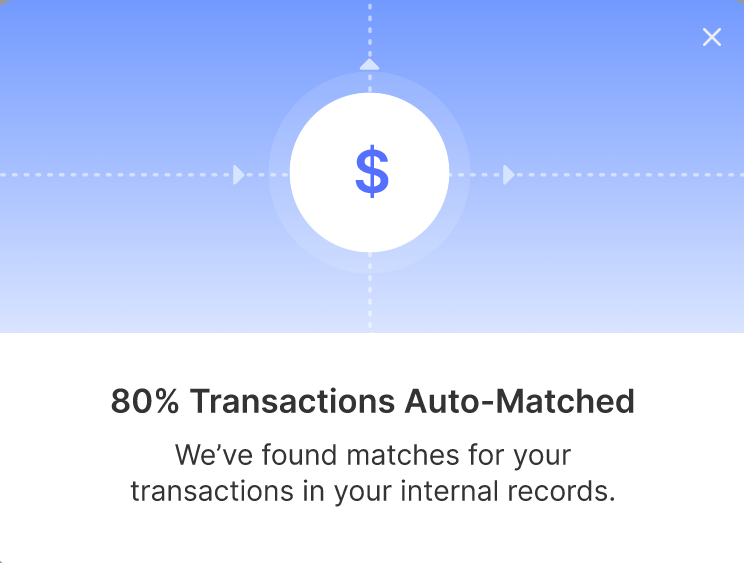
- Automated Matching Algorithms: Deploy automated matching algorithms that compare transaction details from receipts with recorded expenditures in the reconciliation system. These algorithms can identify discrepancies and flag potential errors for further investigation.
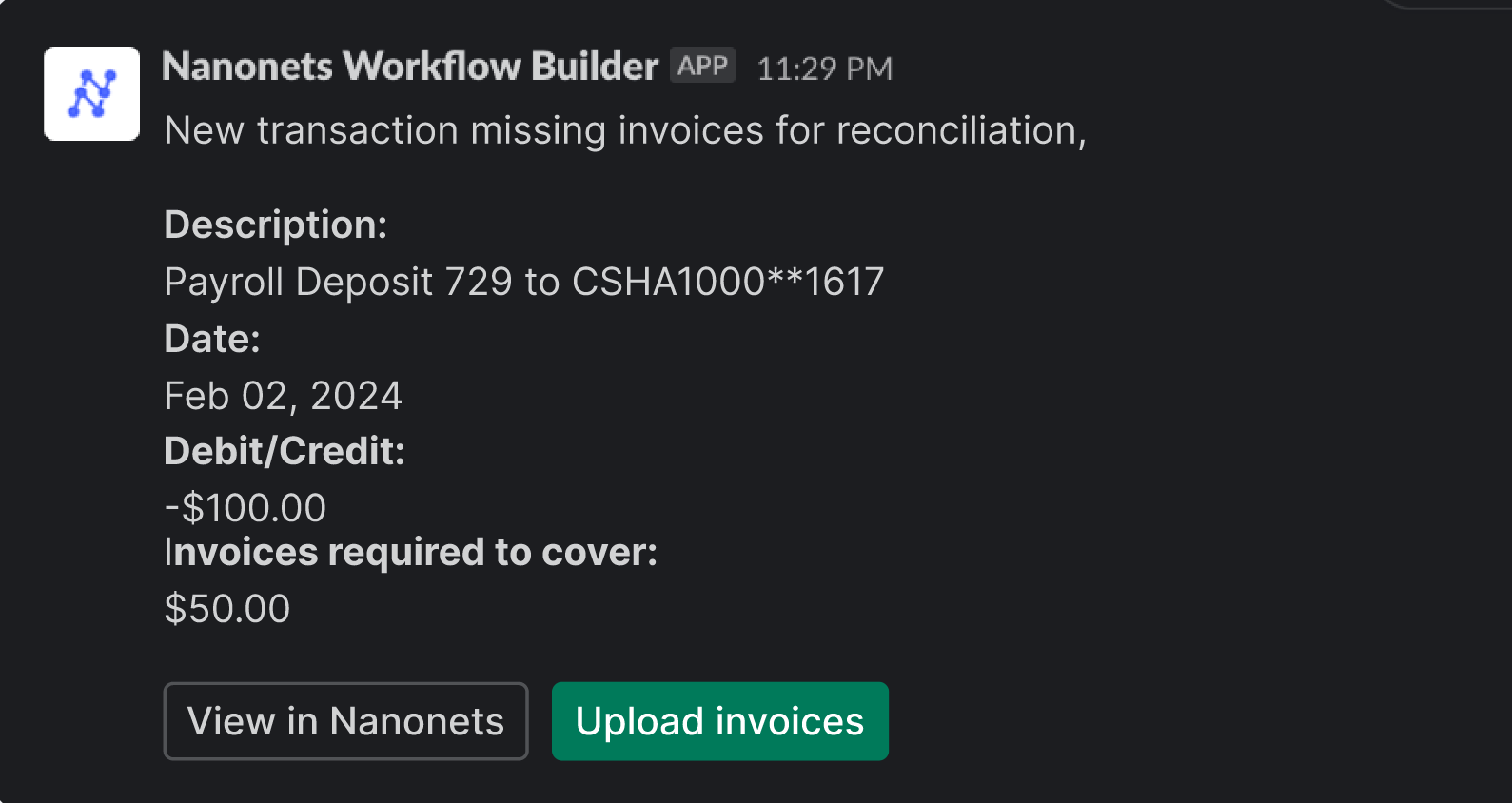
- Workflow Automation: Implement workflow automation tools to streamline the approval process for petty cash expenditures. Define approval hierarchies and set up automated notifications to notify relevant stakeholders when action is required, reducing delays and improving accountability.
- Real-Time Reporting and Dashboards: Utilise real-time reporting capabilities to generate customizable reports and dashboards that provide insights into petty cash transactions, balances, and trends. This allows stakeholders to monitor petty cash activity and identify areas for improvement proactively
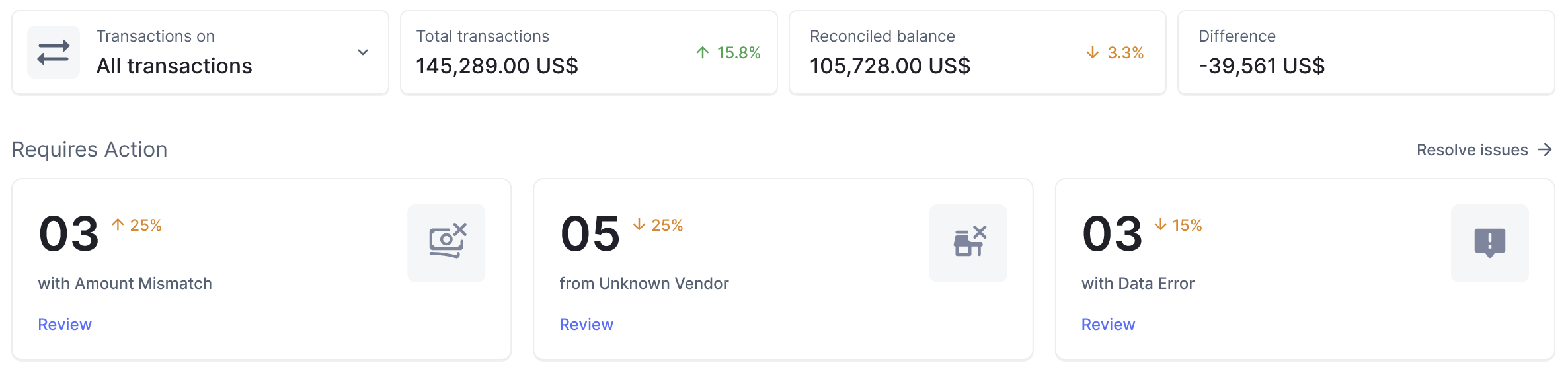
By embracing automation technologies, businesses can transform their petty cash reconciliation processes, reducing manual effort, minimising errors, and enhancing overall efficiency.
Conclusion
Petty cash reconciliation plays a vital role in maintaining accurate financial records and ensuring compliance with internal policies and regulatory requirements. By understanding the challenges associated with petty cash reconciliation and adopting best practices, businesses can optimise their reconciliation processes and mitigate risks effectively.
Furthermore, leveraging automation technologies such as digital receipt management, OCR technology, integration with accounting software, automated matching algorithms, workflow automation, and real-time reporting can streamline petty cash reconciliation and improve accuracy and efficiency.
As businesses continue to evolve and embrace digital transformation, investing in automation solutions for petty cash reconciliation can yield significant benefits, including time savings, cost reduction, enhanced control, and improved decision-making. By prioritizing automation, businesses can optimize their petty cash management processes and focus on driving growth and innovation.



